Spending on hospitals
Public and private hospitals are funded from sources, including the Australian Government, state and territory governments, private health insurance funds and out-of-pocket payments by individuals. Hospitals vary in the types of services they provide, the patients they treat, funding sources, and other factors.
How much is spent on hospital care?
In 2021–22, $96.0 billion ($3,725 per person) was spent on hospital care in Australia (ABS, 2023). Individual spending per person on hospital care increased by an average of 0.3% per year between 2016-17 and 2021–22, after adjusting for inflation.
The $96.0 billion spent on hospitals in 2021–22 accounted for 40% of all health expenditure ($241.3 billion) and is comprised of an estimated:
- $43.8 billion (46%) from state and territory governments
- $34.9 billion (36%) from the Australian Government
- $17.2 billion (18%) from non-government sources (Figure 1).
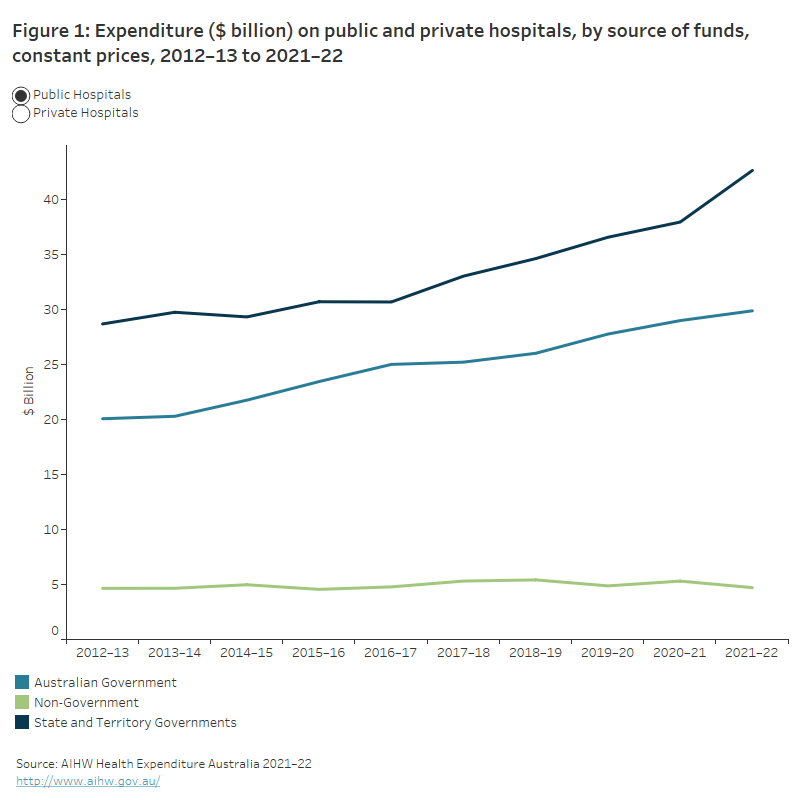
The line chart shows the expenditure on public and private hospitals by the Australian Government, state and territory governments and non-government entities over the period of 2012–13 to 2021–22. Over this period, state and territory governments consistently spent the most on public hospitals whilst non-government entities consistently spent the most on private hospitals. In 2021–22, the Australian Government spent $29.9 billion and $5.1 billion on public and private hospitals respectively compared with state and territory governments who spent $42.6 billion and $1.2 billion respectively and non-government entities who spent $4.7 billion and $12.5 billion respectively.
Public hospitals
In 2021–22, a total of $77.2 billion was spent on public hospitals in Australia by:
- state and territory governments – $42.6 billion (55%)
- Australian Government – $29.9 billion (39%)
- non-government entities – $4.7 billion (6.1%) (including individuals and private health insurers).
State and territory governments, which have primary responsibility for administering public hospitals, contributed the most funding.
Between 2011–12 and 2021–22, Australian Government expenditure on public hospitals increased 3.8% per year on average and state and territory expenditure increased 4.1% per year on average.
Private hospitals
In 2021–22, an estimated total of $18.8 billion was spent on private hospitals by:
- private health insurance providers – $8.9 billion (47%)
- Australian Government – $5.1 billion (27%)
- individuals – $2.2 billion (12%)
- other non-government – $1.4 billion (7.4%)
- state and territory governments – $1.2 billion (6.5%).
Sixty-seven per cent ($12.5 billion) of private hospital spending came from the non-government sector.
Between 2011–12 and 2021–22, total funding increased by an average of 2.6% each year. The proportion of funding provided by the Australian Government increased 0.3% and funding from state and territory governments increased, on average, 7.0%.
More information about the data
Health Expenditure Australia 2021–22
Australian Government expenditure on hospital care listed in this section excludes Medicare Benefits Schedule (MBS) and some Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme (PBS) spending that relates to services provided in hospitals and that have not historically been treated as hospital spending.


