Income and finances
Exploring the income of a population group can provide insights into their economic security. Generally, a person’s resources are accumulated over the course of their working lives and income levels can diminish during retirement, even as wealth or assets may not.
Many older Australians (aged 65 and over) receive government assistance through a range of payments to help support them financially. This page investigates the types and levels of income received by older people. Throughout this page, ‘older people’ refers to people aged 65 and over. Where this definition does not apply, the age group in focus is specified. The ‘Older Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people’ feature article defines older people as aged 50 and over. This definition does not apply to this page, with Indigenous Australians aged 50–64 not included in the information presented.
Economic security
Economic security is having a stable income or other resources to support a standard of living and cover essential needs, both now and in the immediate future. Essential needs might include food, basic shelter, clothing, hygiene, health care and education (ICRC 2015).
Sources of income
People can receive income from multiple sources. To simplify this, the main source or sources of income that make up the largest proportion of an individual’s total income can be reported. This can be associated with people’s economic security and their socioeconomic circumstances.
The 2018 ABS Survey of Disability, Ageing and Carers reported that for older Australians (aged 65 and over) with an income source, the main source of income was:
- government pension or allowance (57%), decreasing from 63% in 2015
- superannuation, annuity or private pension (21%), increasing from 18% in 2015
- wages or salary (8%), increasing from 7% in 2015 (ABS 2019) (see Figure 10.1).
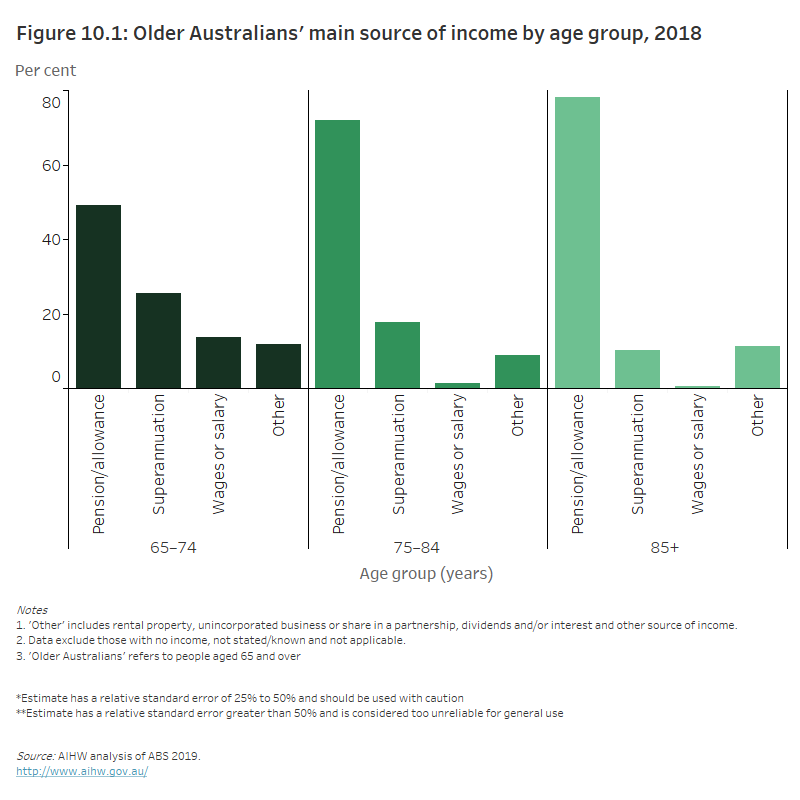
Figure 10.1: Older Australians’ main source of income by age group, 2018
The column chart shows that in 2018 the main source of income across all age groups 65 and over was by receiving a government pension or allowance. 49% of people aged 65–74 received a government pension or allowance as their main source of income and this increased to 78% for people aged 85 and over
Income and wealth
Income and wealth are 2 important concepts in determining a person’s economic resources. Income can be used to purchase goods and services, or saved and invested to increase wealth (ABS 2019). Wealth includes assets such as housing, superannuation, shares, savings and non-financial assets such as cars (Davidson et al. 2020). Generally speaking, incomes increase until around middle age, and wealth gradually increases during working years and is used during retirement (ABS 2019). As a result, in the older years in particular, people can have low incomes but high wealth.
During 2017–18, older people were more likely than younger people to be in low-income households, with 2 in 3 (66%) households with a reference person aged 65 years or over being in the lowest 40% of households as ranked by equivalised disposable income. The average wealth of these older households, however, was 1.5 times that of younger age group households ($1.4 million compared with $0.9 million, respectively). The main reason for this wealth difference is home ownership, with older people having houses of an average value of $597,000 compared with $328,000 for households with a reference person under 65 years (Davidson et al. 2020).
Key terms
Gross income (or total income) is the sum of income received from all sources before any deductions are removed. Equivalised disposable income refers to income whereby the following adjustments are made:
- Income tax is removed resulting in after-tax income (disposable).
- This disposable income is adjusted down based on the size of the household (equivalised). Note no adjustment is made for lone person households (Davidson et al 2020).
Income support payments
There are a range of government assistance payments available to support older Australians. The most common is the Age Pension – an income support payment for people who have reached Age Pension age (65.5 in 2017, 66.5 in July 2021, increasing to 67 in 2023), are under the income and assets test limits, and are an Australian resident (for at least 10 years). Among older Australians, recipient numbers for Jobseeker Payment, Disability Support Pension and Carer Payment have risen steeply in recent years as the qualifying age for Age Pension continues to increase (AIHW 2021b).
At June 2021, 2.8 million people aged 65 and over received an income support payment, equating to 2 in 3 (67%) of the population aged 65 and over (DSS 2021). Of these older people:
- The majority received the Age Pension (93%, 2.6 million).
- 1 in 29 received the Disability Support Pension (3.7%, 101,800).
- 1 in 50 received the Carer Payment (2.0%, 56,400).
- 1 in 83 received the JobSeeker Payment (1.1%, 30,300) (DSS 2021).
At June 2018, there were 2.6 million older people receiving an income support payment. Of these older people:
- The majority received the Age Pension (95%, 2.5 million).
- 2.8% received the Disability Support Pension (72,600).
- 1.8% received Carer Payment (46,400).
- 0.4% received Newstart Allowance (an unemployment-related payment) (10,600 people) (DSS 2018).
Between March 2018 and March 2021, the number of older people receiving the Disability Support Pension increased by 43% and recipients of the JobSeeker Payment and Newstart Allowance tripled, as the qualifying age for the Age Pension continued to rise. At March 2021, the proportion of the population aged 65 and over who received the Age Pension increased with age, up to age group 80–84:
- 38% for those aged 65–69
- 64% for those aged 70–74
- 82% for those aged 80–84.
For those 85 and over, the proportion dropped to 77% (AIHW 2021b).
Housing assistance
Sometimes people need help to meet the cost of housing. Government assistance is available to people on lower incomes, for example those who are renting or saving a deposit for a home purchase.
At 26 June 2020:
- 1 in 5 (20%) income units receiving Commonwealth Rent Assistance had a reference person aged 65 and over, compared with more than 1 in 4 where the reference person was aged 45–64 (27%)*
- 1 in 20 (5.1%) households receiving Private Rent Assistance had a main applicant 65 years and over compared with nearly 1 in 4 aged 45–64 (23%)
- 1 in 10 (11%) households receiving Home Purchase Assistance had a main applicant aged 65 years and over compared with 1 in 3 aged 45–64 (34%) (AIHW 2021a).
An income unit refers to a grouping of one or more people who are in receipt of a social security or family assistance payment, and are assumed to share income with one another. The grouping could comprise a single individual, or a couple, with or without dependent children. As an income unit may be in receipt of more than one payment, one non-dependent member of the unit is designated as its reference person, according to a hierarchy of payment types, with pensions outranking other payments (and the Disability Support Pension and Carer Payment outranking the Age Pension). As a result, the number of income units with reference persons aged 65 and over would be smaller than the number of income units containing members aged 65 and over.
For more information on older Australians’ housing situation, see Housing and living arrangements.
Income during retirement
The age at which a person can access Australia’s Age Pension or superannuation is often referred to as ‘retirement age’ (depending on circumstances, between ages 55 and 67). While people can choose to retire at any age for any reason, the most common reason retirees left their previous job in 2018–19 was reaching ‘retirement age’ or being eligible for superannuation (46%) (ABS 2020).
The Survey of Retirement and Retirement Intentions reported that, in 2018–19, for people aged 45 and over:
- 36% of retired women relied on their partner’s income to meet their living costs at retirement (compared with 7% of retired men).
- For people who were intending to retire, financial security was the main factor that influenced their decision about when to retire (ABS 2020).
Of the 3.9 million retirees in Australia in 2018–19 aged 45 and over, the average age of retirement was 55.4. Around 2 in 5 (44%) women and 1 in 2 (49%) men had a government pension or allowance as their main source of income. Superannuation was the main source of income for a considerable proportion of retirees, especially men (30% for men and 17% for women). Women were far more likely than men to report no personal income (30% for women and 7% for men) (ABS 2020; AIHW 2021b).
Superannuation and other assets
Access to superannuation to supplement the Age Pension is important for older people’s economic security. In 2018–19, around two-thirds (67%) of retirees reported that they had made contributions to a superannuation scheme (76% of men and 59% of women) (ABS 2020). In 1997, 12% of retired Australians aged 45 and over stated that superannuation was their main source of income, compared with 23% in 2018–19 (ABS 2020; AIHW 2015). It is likely that many older Australians were working before superannuation schemes (like those that align with the Superannuation Guarantee (Administration) Act 1992) became mandatory and nationwide.
Older people’s most significant asset is often their home. For more information on older Australians and home ownership, see Housing and living arrangements.
Where do I go for more information?
For more information on the income and finances of older Australians, see:
ABS (Australian Bureau of Statistics) 2019. Disability, Ageing and Carers, Australia: summary of findings 2018. ABS cat. no. 4430. Canberra: ABS. Viewed 2021.
ABS 2020. Retirement and retirement intentions, Australia, 2018–19. Canberra: ABS. Viewed 2020-21.
AIHW (Australian Institute of Health and Welfare) 2015. Australia’s welfare 2015. Australia’s welfare series no. 12. Cat. no. AUS 189. Canberra: AIHW. Viewed 2020-21.
AIHW 2020. People with disability in Australia 2020. Cat. no. DIS 72. Canberra: AIHW. Viewed 2020-21.
AIHW 2021a. Housing assistance in Australia. Cat. no. HOU 325. Canberra: AIHW. Viewed 2021.
AIHW 2021b. Australia’s welfare 2021. Australia’s welfare series no. 15. Canberra: AIHW. Viewed 2021.
Davidson P, Bradbury B, Wong M and Hill T 2020. Inequality in Australia, 2020 Part 2: who is affected and why. Sydney: Australian Council of Social Service and Sydney: University of New South Wales. Viewed 2020-21.
DSS (Department of Social Services) 2018. DSS payment demographic data June 2018. Canberra: DSS.
DSS 2021. DSS payment demographic data June 2021. Canberra: DSS. Viewed October 2021.
ICRC (International Committee of the Red Cross) 2015. What is economic security? Geneva: ICRC. Viewed 18 March 2021.


