Summary
Good health is important – it influences not just how we feel, but also how we go about our everyday lives. Health can mean different things to different people but is widely accepted to be much more than the presence or absence of disease.
Health incorporates our physical, mental and social wellbeing, and is influenced by many determinants such as our: health behaviours, physical environment, social connections, biomedical factors, cultural background, commercial and digital environments, socioeconomic circumstances, access to timely and quality health care programs and services, and genetics.
How has COVID‑19 affected our health?
Chapter two discusses how COVID‑19 is continuing to affect the health and wellbeing of Australians. While people who contract COVID‑19 now are less likely to be hospitalised or die than at the start of the pandemic, the large number of cases that have occurred to date in 2022 produced a much larger number of hospitalisations and deaths than in the first 2 years.
Since the start of the pandemic until 30 April 2022, Australia had reported:
nearly 6 million confirmed cases of COVID‑19

more than 7,000 COVID‑19 related deaths
What are the main causes of death?
Over the last century, death rates have continuously declined but the leading – or main – causes of death have changed: generally, deaths from infectious diseases have decreased, while deaths from chronic conditions, such as cancers and dementia, have increased.
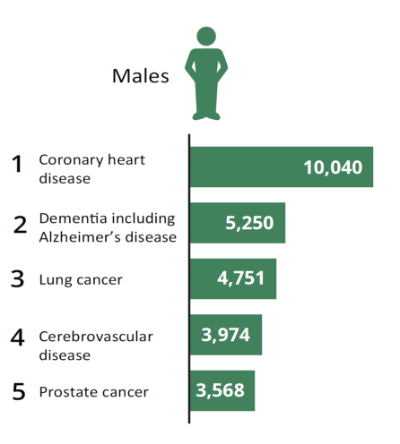
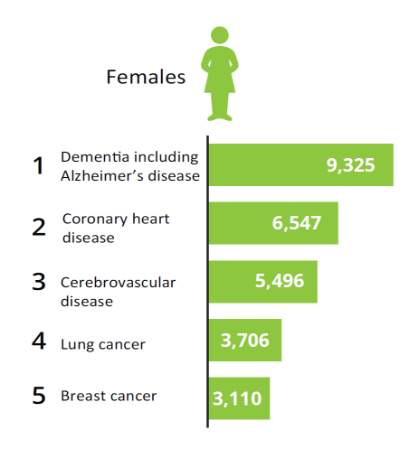
For example in 2020, the leading causes of death among males and females were:
PDF chapter summaries
Good health is important – it influences not just how we feel, but also how we go about our everyday lives. This chapter aims to introduce and conceptualise health.
This chapter highlights the direct impacts of COVID-19 in Australia – including the number of cases, hospitalisations and deaths – from the start of the pandemic until April 2022.
It also summarises key findings related to overall mortality, the prevalence of various diseases and injuries, and forgone or delayed health care.
Based on the latest available data, this chapter summarises the health status of Australians by highlighting key findings and trends across a range of areas, including:
- Life expectancy
- Causes of death
- Burden of disease
- Chronic conditions
- Suicide and intentional self-harm.
Many serious health issues, including some chronic conditions, are related to health behaviours and lifestyle factors that could be prevented or modified.
This chapter provides details on selected risk factors that contribute to disease burden in Australia, including:
- Tobacco smoking
- Alcohol consumption
- Overweight and obesity
- Physical inactivity
- Diet
- Family domestic and sexual violence.
It also highlights the impact of the built and natural environment on our health and wellbeing.
This chapter focuses on Australia’s health system and health service use. In particular, it summarises our:
- Health expenditure
- Health workforce
- Primary, specialist and allied health care
- Hospital care.
For Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people, good health is more than the absence of disease or illness; it is a holistic concept that includes physical, social, emotional, cultural, spiritual and ecological wellbeing, for both the individual and the community.
This chapter summarises the health status and key trends for Indigenous Australians.
It also summarises the impact of COVID-19 on Indigenous Australians – including the number of cases, hospitalisations and deaths – from the start of the pandemic until May 2022. The chapter reports on changes in the use of health services by Indigenous Australians during the first 18 months of the pandemic.
Most Australians can expect to enjoy long and relatively healthy lives, however, some population groups have different experiences of health than others.
This chapter summarises the health status and key trends and for population groups, including:
- Children
- Young people
- Older people
- People with disability
- People living in rural and remote areas.
This chapter identifies Australia’s ranking among Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) member countries for selected health measures and health risk factors.
This chapter summarises Australia’s health information environment and the impact of COVID-19 on the data landscape.
For the most up-to-date information on COVID-19 visit Department of Health.



