Capital spending
Capital spending is an important component of total health spending. However, capital outlays often relate to relatively high-cost items that have useful lives extending over many years. As such, growth in capital spending from year to year can be difficult to interpret. For example, 2016–17 capital spending estimates were affected by a large amount of capital spending on the new Royal Adelaide Hospital in South Australia. This one-off spending increased 2016–17 data and contributed to the 27.9% decrease in capital spending in 2017–18.
Capital spending on health facilities and investments in 2021–22 was $11.7 billion. Over the decade to 2021–22, spending on capital accounted for around 5.8% of total health spending per year on average (Table 2).
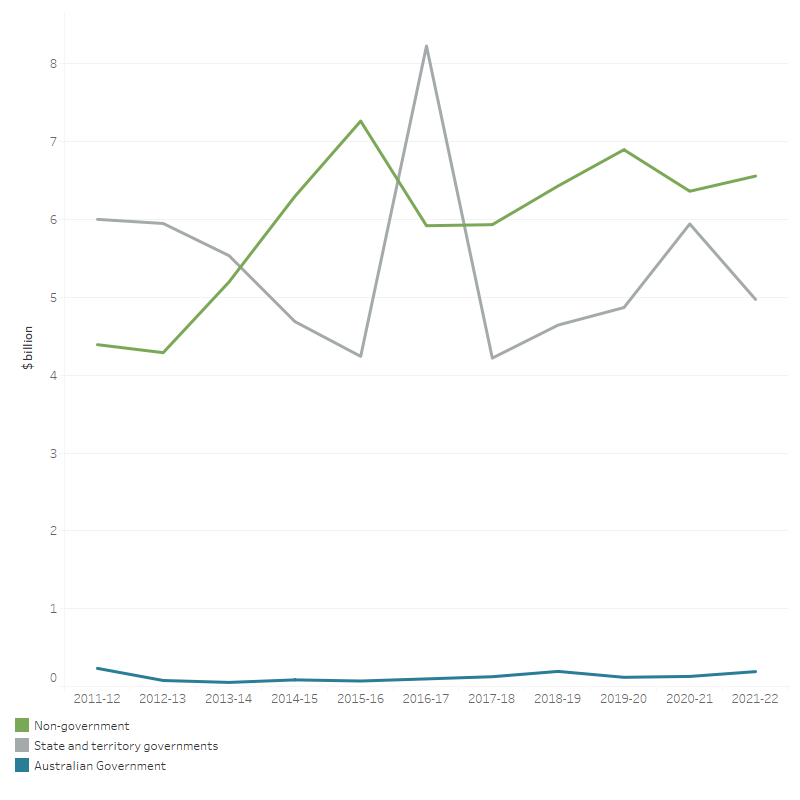
From 2011–12 to 2021–22, capital spending by the non-government sector averaged half (52.0%) of capital spending, state and territory governments averaged 46.9% and the Australian Government averaged 1.1% (Figure 31).
Figure 31: Capital spending, by source of funds, constant prices (a), 2011–12 to 2021–22
The line graph shows that capital spending by state and territory governments and non-government has been volatile in the decade 2011–12 to 2021–22. State and territory government spending on capital decreased from $6.0 billion in 2011–12 to $4.2 billion in 2015–16 before spiking to $8.2 billion in 2016–17 and was $5.9 billion in 2020–21 then decreased to 5.0 billion in 2021–22. Non-government spending on capital fluctuated over the decade from $4.4 billion in 2011–12 to $6.6 billion in 2021–22. Australian Government spending on capital has been low and steadily increased over the same period, at $200 million in 2021–22.
(a) Constant price health spending is in 2021–22 prices.
Notes:
- Non-government spending on capital is by other non-government only, with no spending by individuals or private health insurance providers.
- The increase in 2016–17 for state and territory governments was due to a one-off capital spending project in South Australia.
Source: AIHW Health Expenditure Database (Table 36).


