Hospital funding and expenditure
This section includes information about sources of funds for public and private hospitals, and how they spent the money.
How were hospitals funded?
Hospital funding is the money received by hospitals to pay for the services they provide. Public and private hospitals receive funding from Australian Government, state and territory governments, private health insurance funds and out-of-pocket payments by individuals.
Public and private hospitals are funded from a range of sources, reflecting the types of patients they treat and the services they provide.
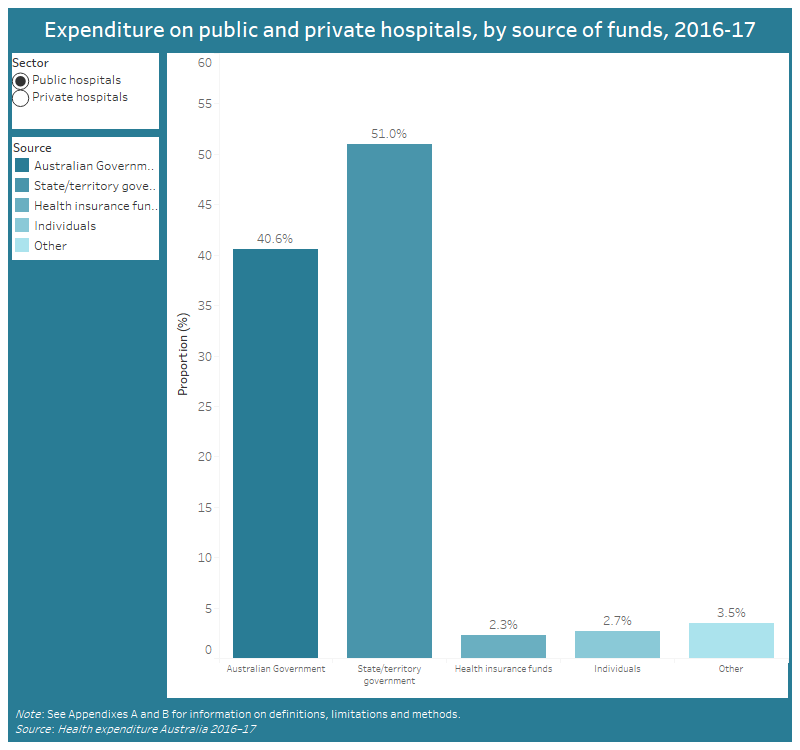
Public hospitals
In 2016–17, the state and territory governments and the Australian Government funded about 92% of care in public hospitals.
Between 2012–13 and 2016–17, funding increased by an average of 1.8% each year, and the proportion of funding by the Australian Government increased from 37% to 41%.
See the ‘Funding source’ visualisation above for more information.
Private hospitals
In 2016–17, private health insurance and out-of-pocket payments by patients funded about 69% of care in private hospitals.
Between 2012–13 and 2016–17, funding increased by an average of 2.9% each year and the proportion of funding provided by the Australian Government decreased from 30% to 24%.
How much did hospitals spend?
Hospital expenditure is the money spent by hospitals on the goods and services they use, such as salaries and wages, drugs, medical and surgical supplies, payments to visiting medical officers and other administrative expenses.
Public hospitals
In 2017–18:
- $71 billion (excluding depreciation) was spent on public hospital services
- about 60% spent on salaries and wages and 55% on admitted patient care.
Private hospitals
In 2016–17:
- $14 billion (including depreciation) was spent on private hospitals
- almost 49% was spent on salaries and wages.
Between 2012–13 and 2016–17, recurrent expenditure by private hospitals increased by an average of 4.5% per year (after adjusting for inflation).
Sources of funding for admitted patient episodes
Between 2013–14 and 2017–18, private health insurance-funded hospitalisations increased by an average of 3.6% each year, and public patient hospitalisations increased by an average of 4.7%.
In 2017–18:
- more than half (52%) of separations in all hospitals were for Public patients and 42% were for Private health insurance patients
- 83% of public hospital separations were for Public patients
- 82% of private hospital separations were for Private health insurance patients
- 69% of Department of Veterans’ Affairs funded separations occurred in private hospitals.
Where to go for more information
For more information on the funding of Australia’s hospitals, see Health expenditure Australia 2016–17.
For more information on recurrent expenditure on public hospital services, see Hospital resources 2017–18: Australian hospital statistics.
For more information on admitted patient funding sources, see Chapter 7 of Admitted patient care 2017–18: Australian hospital statistics.
For more information on recurrent expenditure on private hospitals, see Private hospitals, Australia, 2016–17.


