Classification of maternal deaths
In Australia, after review of all available information regarding a maternal death a multi-disciplinary maternal mortality committee classifies the death as a direct or indirect maternal death. Direct maternal deaths are those that result directly from complications of pregnancy or its management, such as obstetric haemorrhage. Indirect maternal deaths are those that are due to pre-existing disease but where disease progression was influenced by pregnancy, such as maternal heart disease aggravated by the pregnancy. Deaths considered to be unrelated to pregnancy are classified as incidental deaths.
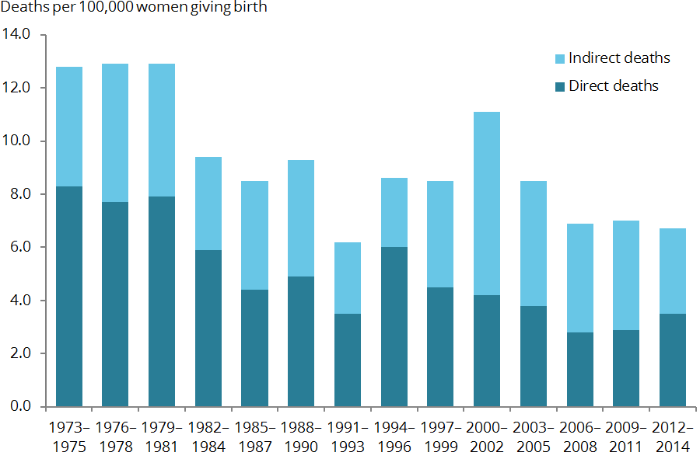
The Australian maternal death trends between 1973–1975 and 2012–2014 are shown in figure 3. The incidence of both direct and indirect maternal deaths have decreased over this period of time. The overall MMR has decreased from 12.7 per 100,000 women giving birth in 1973–1975 to 6.8 per 100,000 women giving birth in 2008–2012 (a 46% reduction), with the majority of that reduction being related to direct maternal deaths (the direct MMR has decreased from 8.3 per 100,000 women giving birth in 1973–1975 to 3.5 per 100,000 women giving birth in 2008–2012 (a 58% reduction). The indirect MMR has shown less change, from 4.5 per 100,000 women giving birth in 1973–1975 to 3.2 per 100,000 women giving birth in 2008–2012 (a 29% reduction).
Figure 3: Classification of maternal deaths, Australia 1973–1975 to 2012–2014