Multiple risk factors
Risk factors for chronic kidney disease (CKD) rarely act alone or independently. Many also apply to other chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes, which in turn are risk factors for CKD. CKD risk factors tend to coexist and to interact in their effects (AIHW 2021, White 2020). The more risk factors a person has, the greater their risk of developing chronic disease, including CKD (Licher et al. 2019).
Based on pooled data from the ABS 2014–15 and 2017–18 National Health Surveys:
- 76% of Australian adults had at least 1 of 5 key CKD risk factors – either diabetes, uncontrolled high blood pressure, heart, stroke and vascular disease, current smoker or overweight/obese
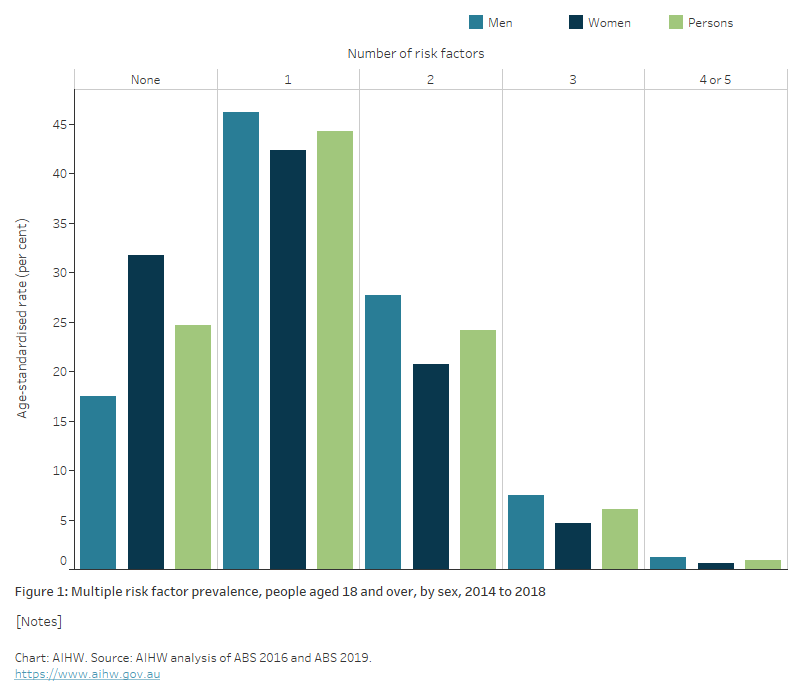
- 25% had 2 of these risk factors in combination, while 7.4% had 3 or more of these risk factors in combination (Figure 1)
- men (37%) were more likely than women (27%) to have 2 or more of these risk factors in combination (AIHW analysis of ABS 2016 and ABS 2019).
Figure 1: Multiple risk factor prevalence, people aged 18 and over, by sex, 2014–2018
The bar chart shows the distribution of number of risk factors in 2014–18, with men (37%) more likely than women (27%) to have 2 or more of these risk factors in combination.
Co-occurrence of 3 key risk factors
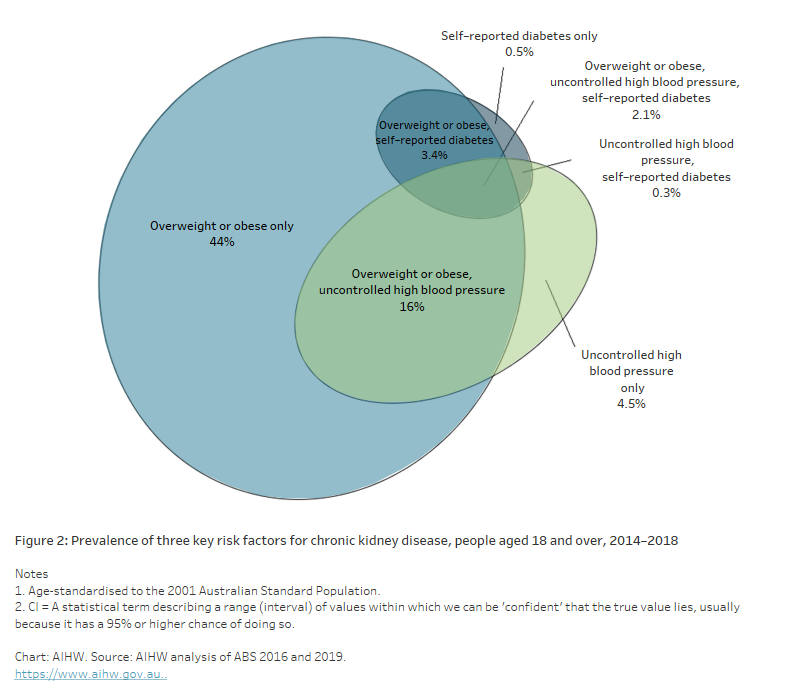
Many adults who are overweight or obese also have uncontrolled high blood pressure, and have diabetes, placing them at increased risk of CKD development and progression (Figure 2).
Based on pooled data from the ABS 2014–15 and 2017–18 National Health Surveys, an estimated:
- 13 million adults (71%) had at least 1 of these 3 risk factors (men 77%, women 64%)
- 2.9 million adults (16%) were overweight or obese and had uncontrolled high blood pressure (men 18%, women 14%)
- 624,000 adults (3.4%) were overweight or obese and self-reported having diabetes (men 4.0%, women 2.9%)
- 383,000 adults (2.1%) were overweight or obese, had uncontrolled high blood pressure, and self-reported having diabetes (men 2.4%, women 1.8%) (AIHW analysis of ABS 2016 and ABS 2019).
Figure 2: Prevalence of three key risk factors for chronic kidney disease, people aged 18 and over, 2014–2018
The Venn diagram shows the overlapping proportion of adults who were overweight/obese, had self-reported diabetes or had uncontrolled high blood pressure in 2014–18. An estimated 44% were overweight or obese only and only 2.1% had all 3 risk factors.
ABS (Australian Bureau of Statistics) (2016) Microdata: National Health Survey, 2014–15, AIHW analysis of detailed microdata, ABS, Australian Government, accessed 20 October 2021.
ABS (2019) Microdata: National Health Survey, 2017–18, AIHW analysis of detailed microdata, ABS, Australian Government, accessed 20 October 2021.
AIHW (2021) Australian Burden of Disease Study 2018: Interactive data on risk factor burden, AIHW, Australian Government, accessed 1 February 2022.
Licher S, Heshmatollah A, van der Willik, KD, Stricker BHC, Ruiter R, de Roos EW, et al. (2019) Lifetime risk and multimorbidity of non-communicable diseases and disease-free life expectancy in the general population: a population-based cohort study, PLOS Medicine, 16(2), e1002741, doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002741.
White SL (2020) Chronic kidney disease, diabetes and cardiovascular disease: evidence report 2021, Kidney Health Australia, Melbourne, accessed 1 February 2022.


