Continuity of carer
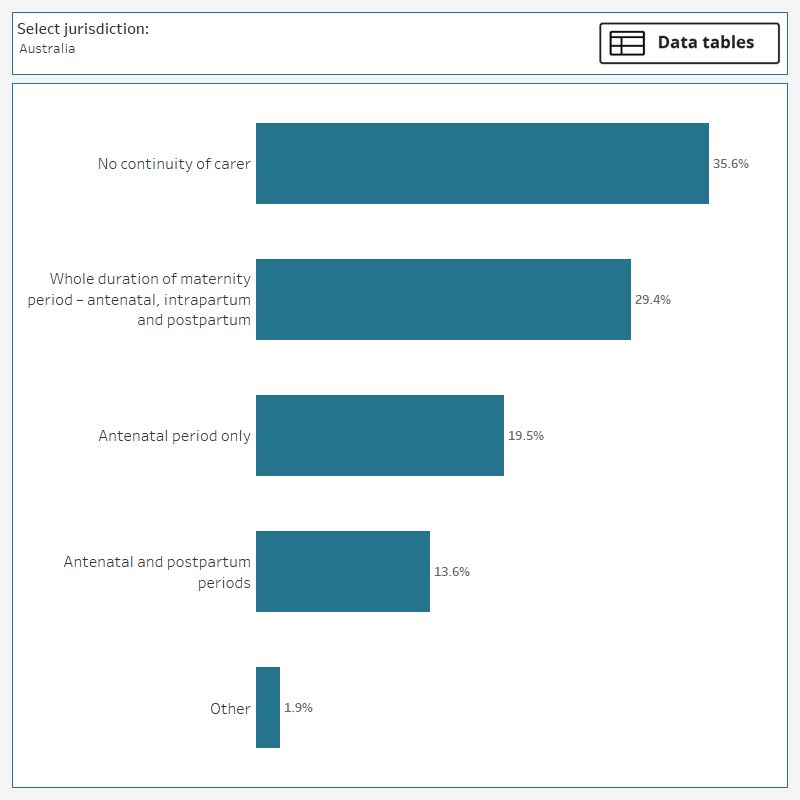
The extent of continuity of carer is a measure of the one-to-one care provided by the same named caregiver across the continuum of maternity care. Over one-third (36%) of models have no continuity of carer in any stage of the maternity period, which means there is no named carer assigned to each woman and care is given by different providers. A similar proportion (35%) have continuity of carer for some part of the maternity period, for example the antenatal period only (19%), or the antenatal and postpartum periods (14%). Around 29% of models have continuity of carer through the whole maternity period, meaning a single named designated carer provides or coordinates care for the antenatal, intrapartum, and postpartum periods. This is higher in Queensland (38%), South Australia (37%), and the Australian Capital Territory (36%) and may be related to the higher number of models classified as midwifery group practice caseload care.
The data visualisation below (Figure 4) shows maternity models of care, by the extent of continuity of carer. Select from the drop-down menu to filter by jurisdiction (state or territory). Use the button to access the data table.
Figure 4: Proportion of models of care, by continuity of carer, Australia, 2023
The bar chart shows over one-third of models of care have no continuity of carer. Around one-third have continuity of carer for some part of the maternity period and less than one-third have continuity of carer through the whole duration of the maternity period.
Notes
- The extent of continuity of carer is a measure of the one-to-one care provided by the same named caregiver across the continuum of maternity care, that is, the antenatal (before birth), intrapartum (birthing) and postpartum (after birth) periods.
- 'Other' includes where there is continuity of carer in the antenatal and intrapartum periods only, or the intrapartum and postpartum periods only.
- Analyses are based on the models of care being used by maternity services with birthing facilities that were classified in the MoC NBPDS in June 2023.
Source: AIHW analysis of the MoC NBPDS.
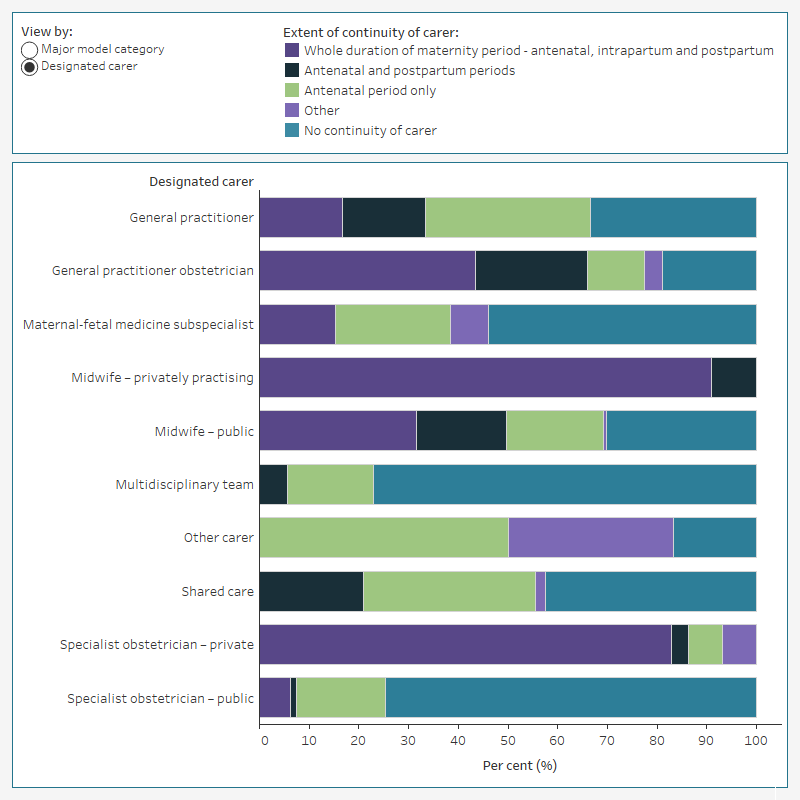
The extent of continuity of carer varies by model category. Models classified as midwifery group practice caseload care, by definition, have continuity of carer across the whole duration of the maternity period. Models classified as private midwifery care, and private obstetrician specialist care also have a high level of continuity of carer across the whole duration of the maternity period (100% and 90% of models in these categories, respectively). In contrast, models classified as team midwifery care, by definition, have no continuity of carer at any stage of the maternity period. Models classified as public hospital maternity care, or public hospital high-risk maternity care, or shared care are more likely to have no continuity of carer (56%, 54% and 42% of models in these categories, respectively).
The extent of continuity of carer also varies by the type of designated carer. Models of care with a designated carer of midwife – privately practising, or specialist obstetrician – private, are more likely to have continuity of carer across the whole duration of the maternity period (91% and 83%, respectively). In contrast, three-quarters (75%) of models of care with a designated carer of specialist obstetrician – public have no continuity of carer at any stage of the maternity period.
The data visualisation below (Figure 5) shows the extent of continuity of carer by major model category and designated carer. Change the display by selecting either major model category or designated carer.
Figure 5: Continuity of carer, by major model category and designated carer, Australia, 2023
There are two bar charts in the data visualisation. The first chart shows models classified as midwifery group practice caseload care have continuity of carer across the whole duration of the maternity period. Most (90%) models classified as private obstetrician specialist care also have continuity of carer across the whole duration of the maternity period. In contrast, models classified as team midwifery care have no continuity of carer at any stage of the maternity period and models classified as public hospital maternity care or public hospital high-risk maternity care are also more likely to have no continuity of carer (56% and 54% of models in these categories, respectively). The second chart shows models with a designated carer of midwife – privately practising or specialist obstetrician – private, are more likely to have continuity of carer across the whole duration of the maternity period (91% and 83%, respectively). In contrast, models of care with a designated carer of specialist obstetrician – public are more likely to have no continuity of carer at any stage of the maternity period (75%).
Notes
- The extent of continuity of carer is a measure of the one-to-one care provided by the same named caregiver across the continuum of maternity care, that is, the antenatal (before birth), intrapartum (birthing) and postpartum (after birth) periods.
- 'Other' includes where there is continuity of carer in the antenatal and intrapartum periods only, or the intrapartum and postpartum periods only.
- Whole duration of maternity period includes the antenatal (before birth), intrapartum (at birth) and postpartum (after birthing) periods.
- Analyses are based on the models of care being used by maternity services with birthing facilities that were classified in the MoC NBPDS in June 2023.
Source: AIHW analysis of the MoC NBPDS.


