QIM 8: Proportion of eligible regular clients with a record of the necessary risk factors in their GP record for CVD risk assessment
Assessment of absolute CVD risk based on multiple risk factors is more accurate than that based on individual risk factors due to the cumulative nature of risk effects. Absolute CVD risk assessment combines risk factors to calculate the probability that an individual will develop a cardiovascular event or other vascular disease within a specified time frame, usually 5 years (RACGP 2018). The risk assessment is useful for measuring risk in asymptomatic clients without established CVD (i.e. for primary prevention). Clients aged 45–74 years with established CVD and/or several other conditions who are already clinically determined to be at high risk of a cardiovascular event (NVDPA 2012) have been excluded from the measure as outlined in the PIPQI specification.
Capture of results recorded outside of the general practice setting
Results arising from clinical intervention conducted outside of the service that are known and recorded by the practice are included in the measure. However, sometimes test results recorded elsewhere may not be captured in this report. For example, this might be a result from a specialist service that is not recorded in the clinical information system of the client’s usual general practice due to an incompatible clinical information system between a practice and a specialist service.
Other sources of relevant information
There are other administrative data collections where the relevant data from these client-provider interactions are captured, for example, Medicare Benefits Schedule (MBS) and the National Health Survey (NHS) conducted by the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS).
This indicator reports on the proportion of regular clients aged 45 to 74 years without a CVD diagnosis with 4 risk factors (tobacco smoking status, diabetes type or HbA1c result or fasting glucose tests, blood pressure, lipid levels) recorded in their GP record to enable CVD risk assessment.
During this reporting period, the AIHW became aware of at least 2 different counting rules being applied by extraction tools in the enumeration of regular clients for this indicator.
The POLAR extraction tool used by 5 PHNs applied reference period cut-off dates of 24 months for recording systolic blood pressure and 5 years for recording cholesterol/HDL levels, in line with the RACGP Red Book (RACGP 2018).
In contrast, the CAT4 extraction tool used by 27 PHNs did not apply any reference period cut-off dates for diabetes screening, systolic blood pressure, cholesterol/HDL levels.
As shown in figures 42 to 44, these different methods lead to lower recording results with time restrictions applied, and a higher recording result with no time restrictions applied. These results should be interpreted with caution when comparing results between extraction tools.
QIM 8: Regional proportions
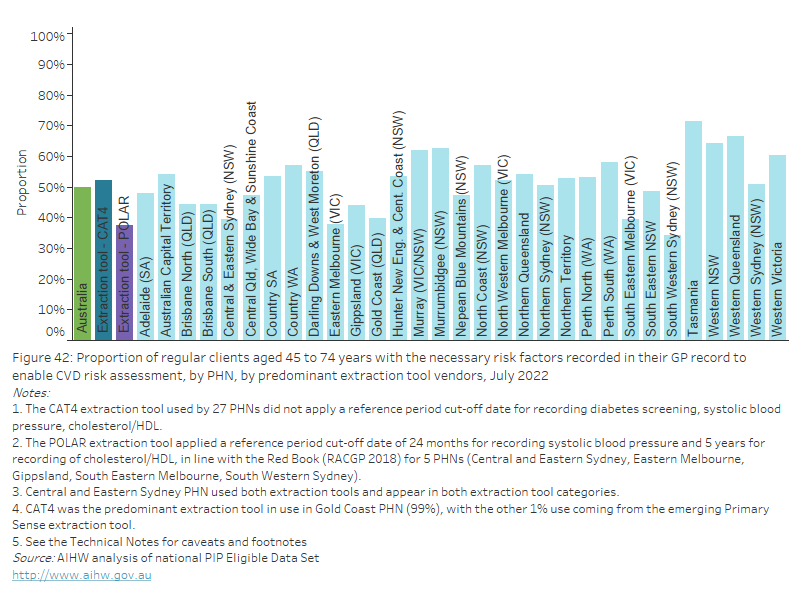
As of July 2022, nationally, 49.8% of regular clients aged 45 to 74 years without a CVD diagnosis had the necessary risk factors recorded in their GP record to enable CVD risk assessment. This varied from 34.2% to 71.3% across PHNs.
Figure 42: Proportion of regular clients aged 45 to 74 years with the necessary risk factors recorded in their GP record to enable CVD risk assessment by PHN, by predominant extraction tool vendors, July 2022
This bar chart shows the proportion of regular clients aged 45 to 74 years with the necessary CVD risk factors recorded in their GP record, by PHN and predominant extraction tool vendors for July 2022.
QIM 8: National proportions over time
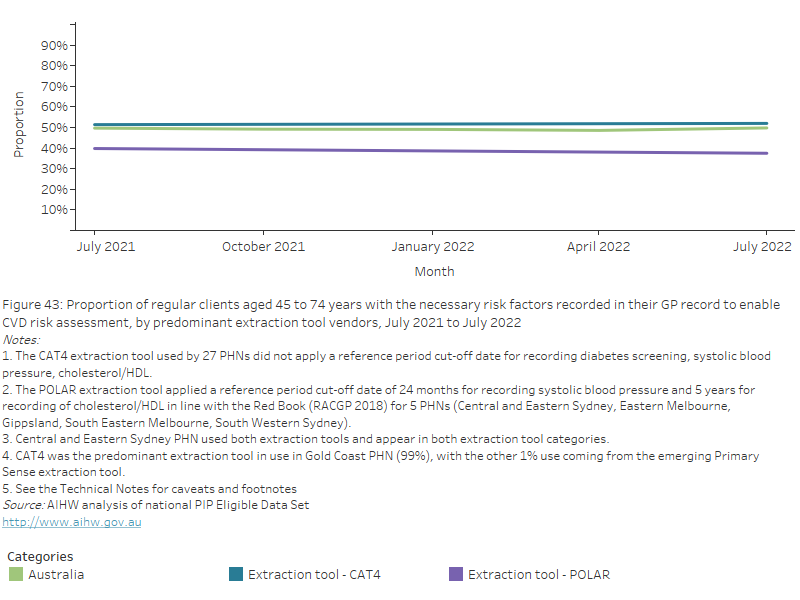
Nationally, by predominant extraction tool pathways, between July 2021 and July 2022, the proportion of regular clients aged 45 to 74 years without a CVD diagnosis who had the necessary risk factors recorded in their GP record to enable CVD risk assessment within:
- CAT4 remained constant at 51.4% and 52.0%
- POLAR decreased by 2.3% from 39.8% to 37.5%.
These results should be interpreted with caution when comparing results between extraction tools.
Figure 43: Proportion of regular clients aged 45 to 74 years with the necessary risk factors recorded in their GP record to enable CVD risk assessment, by predominant extraction tool vendors, July 2021 to July 2022
This line chart shows the proportion of regular clients aged 45 to 74 years with the necessary CVD risk factors recorded in their GP record, by predominant extraction tool vendors, from July 2021 to July 2022.
QIM 8: National proportions by age and sex
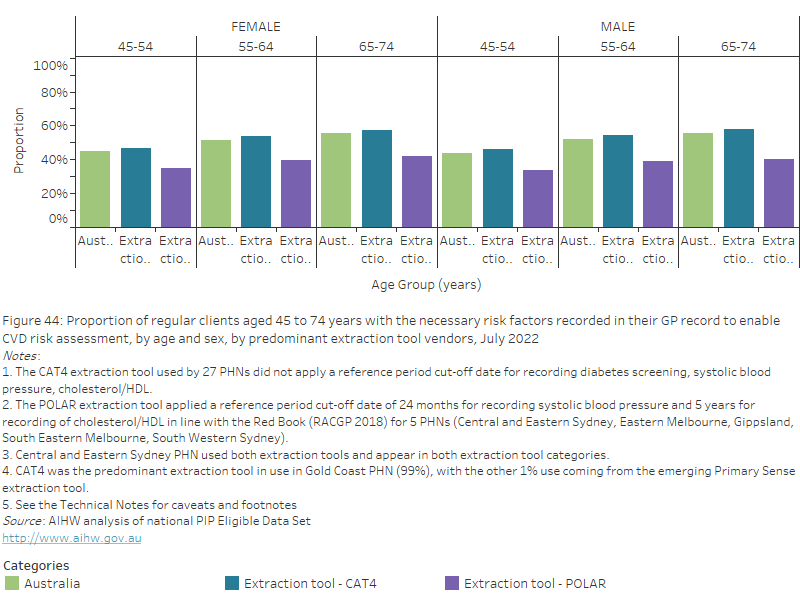
As of July 2022, nationally for all extraction tools combined, the proportion of regular clients aged 45 to 74 years without a CVD diagnosis with the necessary risk factors recorded in their GP record to enable CVD risk assessment increased with age and was:
- highest in the 65–74 years age group for both females (55.3%) and males (55.5%)
- lowest in the 45–54 years age group for both females (44.6%) and males (43.8%).
These results should be interpreted with caution when comparing results between extraction tools.
Figure 44: Proportion of regular clients aged 45 to 74 years with the necessary risk factors recorded in their GP record to enable CVD risk assessment, by age and sex, by predominant extraction tool vendors, July 2022
This bar chart shows the proportion of regular clients aged 45 to 74 years with the necessary CVD risk factors recorded in their GP record, by age, sex, and predominant extraction tool vendors for July 2022.
- Data for clients are included if they have record of necessary risk factors (age, sex, tobacco smoking status, diabetes type or HbA1c result or fasting glucose tests, blood pressure, lipid levels) to assess CVD risk assessment.
- Clinical definitions for CVD vary across clinical information systems, as different coding schemes are used. This may lead to some variation in the number of clients who will be picked up by different systems (Department of Health 2017).
- The reference periods for recording the risk factors of this QIM have been interpreted and coded differently by extraction tool vendors. The POLAR extraction tool used by 5 PHNs, applied reference period cut-off dates of 24 months for recording systolic blood pressure and 5 years for recording cholesterol/HDL levels, in line with the RACGP Red Book (RACGP 2018). In contrast, the CAT4 extraction tool used by 27 PHNs, did not apply any reference period cut-off dates for diabetes screening, systolic blood pressure, cholesterol/HDL levels. For this reason these results should be interpreted with caution when comparing results between extraction tools.
- Eligible clients who do not have a current diagnosis of a cardiovascular condition and have a record of age, sex, tobacco smoking status, systolic blood pressure, diabetes status/diabetes screening test, total cholesterol and HDL cholesterol levels in their GP record are included in the measure.
- Clients are excluded from the measure if they:
- refused measurement,
- have a recorded diagnosis of CVD,
- are regular and without known CVD, but information for ALL risk factors is not recorded.
Department of Health (2017) National Key Performance Indicators for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander primary health care, Department of Health, Canberra, accessed 12 August 2022.
NVDPA (National Vascular Disease Prevention Alliance) (2012) Guidelines for the management of absolute cardiovascular disease risk, accessed 12 August 2022.
RACGP (2018) Guidelines for preventive activities in general practice, 9th edition, updated, RACGP, East Melbourne, Victoria, accessed 10 August 2022.


