QIM 4: Proportion of regular clients aged 65 years and over with an influenza immunisation status recorded in their GP record within the previous 15 months
Influenza is a common disease of the respiratory tract. It affects people of all ages. It is estimated that influenza is likely to be associated with more than 3,000 deaths and 13,500 hospitalisations each year in Australia, just in people aged >50 years (ATAGI 2018).
A number of groups are at a higher risk of influenza and its complications. These groups experience higher rates of illness and death associated with influenza than the rest of the population and adults aged ≥65 years is one of the vulnerable population groups. Therefore, annual influenza vaccination is strongly recommended for those aged ≥65 years (ATAGI 2018). The administration of the influenza vaccine to people at risk of complications of infection is the single most important measure in preventing or attenuating influenza infection and preventing mortality. There is evidence that influenza vaccine reduces hospitalisations from influenza and pneumonia and all-cause mortality in adults aged ≥65 years of age. While best practice guidelines recommend annual immunisation, a 15-month interval allows for cases when a client decides to receive a vaccine earlier than recommended (for example, from a pharmacy), or delay and wait for the release of an ‘enhanced’ vaccine (Department of Health 2020b).
Capture of results recorded outside of the general practice setting
Results arising from clinical intervention conducted outside of the service that are known and recorded by the practice are included in the measure. Where immunisation was provided elsewhere but is not known to the practice, this is not captured in the report. For example, this might be where the vaccination providers’ information systems may not be compatible with the clinical information system of the client’s usual general practice.
Other sources of relevant data
There are other administrative data collections where the data on influenza immunisation are captured, for example, the Australian Immunisation Register (AIR).
This indicator reports on the proportion of regular clients aged 65 years and over who had an influenza immunisation status recorded in their GP record within the previous 15 months.
QIM 4: Regional proportions
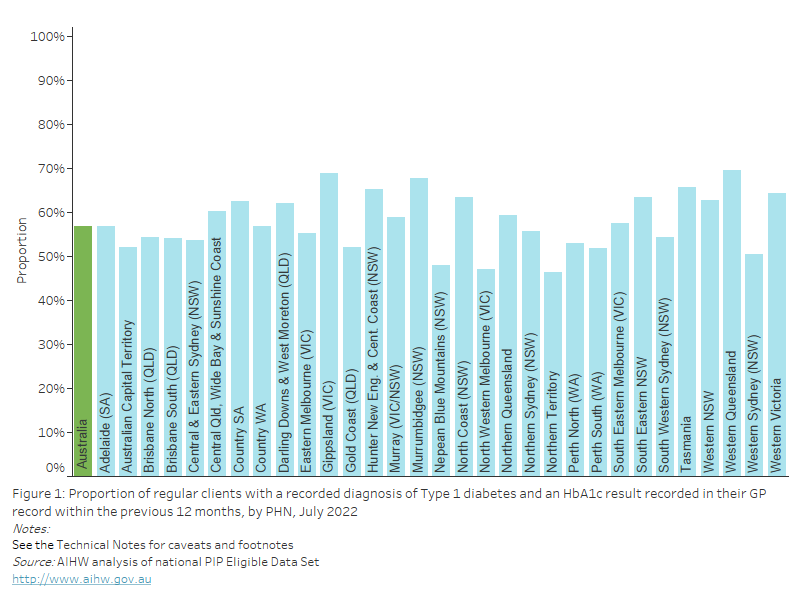
As of July 2022, nationally, 59.9% of regular clients aged 65 years and over had an influenza immunisation status recorded in their GP record in the previous 15 months. This varied from 43.1% to 70.5% across PHNs.
Figure 30: Proportion of regular clients aged 65 years and over with an influenza immunisation status recorded in their GP record within the previous 15 months, by PHN, July 2022
This bar chart shows the proportion of regular clients aged 65 years and over with influenza immunisation status recorded in their GP record, by PHN for July 2022.
QIM 4: National proportions over time
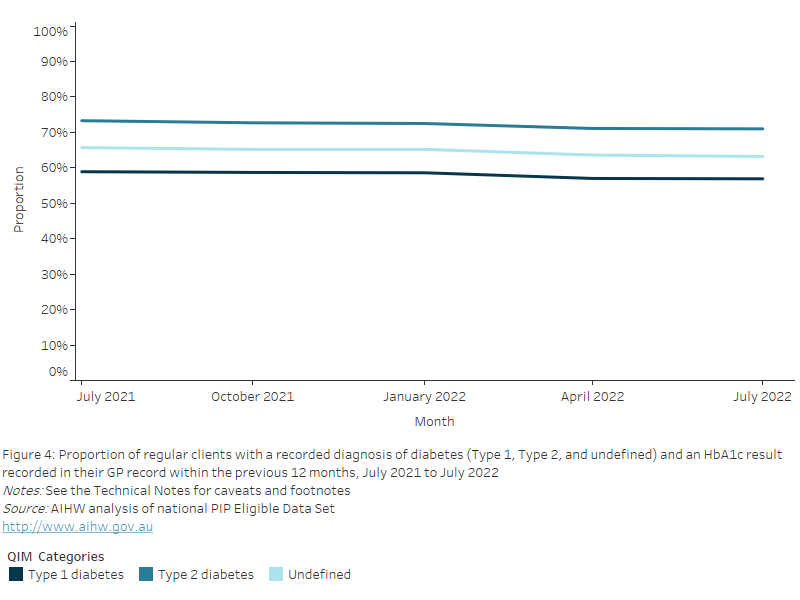
Nationally, between July 2021 and July 2022, there was a decrease of 4.0% of regular clients aged 65 years and over who had an influenza immunisation status recorded in their GP record within the previous 15 months, from 63.9% to 59.9%.
Figure 31: Proportion of regular clients aged 65 years and over with an influenza immunisation status recorded in their GP record within the previous 15 months, July 2021 to July 2022
This line chart shows the proportion of regular clients aged 65 years and over with influenza immunisation status recorded in their GP record, from July 2021 to July 2022.
QIM 4: National proportions by sex
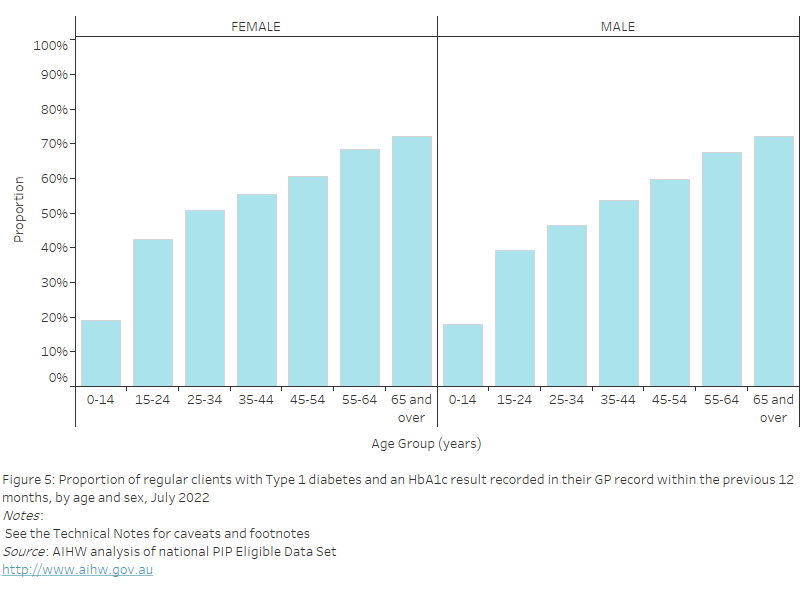
As of July 2022, nationally, the proportion of regular clients aged 65 years and over with an influenza immunisation status recorded in their GP record within the previous 15 months was 60.8% for females and 58.8% for males.
Figure 32: Proportion of regular clients aged 65 years and over with an influenza immunisation status recorded in their GP record within the previous 15 months, by sex, July 2022
This bar chart shows the proportion of regular clients aged 65 years and over with influenza immunisation status recorded in their GP record, by sex for July 2022.
- Data for clients aged 65 and over are included if the client has been immunised against influenza within the previous 15 months.
- Results arising from clinical intervention conducted outside of the service that are known and recorded by the service are included in the measure. Where immunisation was given elsewhere (for example, workplace or pharmacy) and the information is not recorded in the electronic record of the client’s usual general practice, then this may result in an apparent missing information.
- Clients are excluded from the measure if they:
- did not have the immunisation due to documented medical reasons (e.g. allergy), system reasons (vaccine not available), or client reasons (e.g. refusal); or
- had results from measurements conducted outside of the service which were not available to the service.
- There are other administrative data collections where the data on influenza immunisation are captured for example, the Australian Immunisation Register (AIR).
- There was a change in the recording of influenza immunisations identified in January 2022 that resulted in an undercount of the number of regular clients receiving influenza immunisations and a lower proportion reported for this QIM (Pen CS 2022). This change impacted the January 2022 and April 2022 data submissions for selected practices in 27 of the 31 PHNs.
ATAGI (Australian Technical Advisory Group on Immunisation) (2018) Australian Immunisation Handbook, Australian Government Department of Health, Canberra, accessed 15 August 2022.
Department of Health (2020b) Practice Incentives Program Quality Improvement Measures User Guide for General Practices, Department of Health, Canberra, accessed 12 August 2022.
Pen CS (2022) CAT4 Release Notes v4.39 January 2022, accessed 15 August 2022.


