QIM 3: Proportion of regular clients with a current height and weight classification recorded in their GP record and a derived BMI result
On this page:
In 2017–18, two-thirds (67.0%) of Australian adults aged 18 years and over were overweight or obese (12.5 million people) (ABS 2021). Being overweight, obese or underweight is associated with higher rates of morbidity, and overweight and obesity is a major public health issue in Australia. Overweight and obesity are risk factors for Type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, hypertension, osteoarthritis, some cancers and gallbladder disease. Being overweight or obese is also associated with certain psychosocial problems, functional limitations and disabilities. On the other hand, being underweight may cause malnourishment and lead to compromised immune function, respiratory disease, digestive diseases, cancer and osteoporosis.
Other sources of relevant data
Data on measured height, weight and BMI are captured in the National Health Survey (NHS) conducted by the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS).
This indicator contains 2 parts, assessing the proportion of regular clients 15 years of age and older who:
- QIM 3a: had a height and weight measurement recorded in their GP record within the previous 12 months, from which a Body Mass Index (BMI) was derived.
- QIM 3b: had their BMI classified as either underweight, healthy, overweight or obese derived from the current height and weight recorded in their GP record.
Proportion of regular clients with a weight classification recorded (QIM 3a)
QIM 3a: Regional proportions
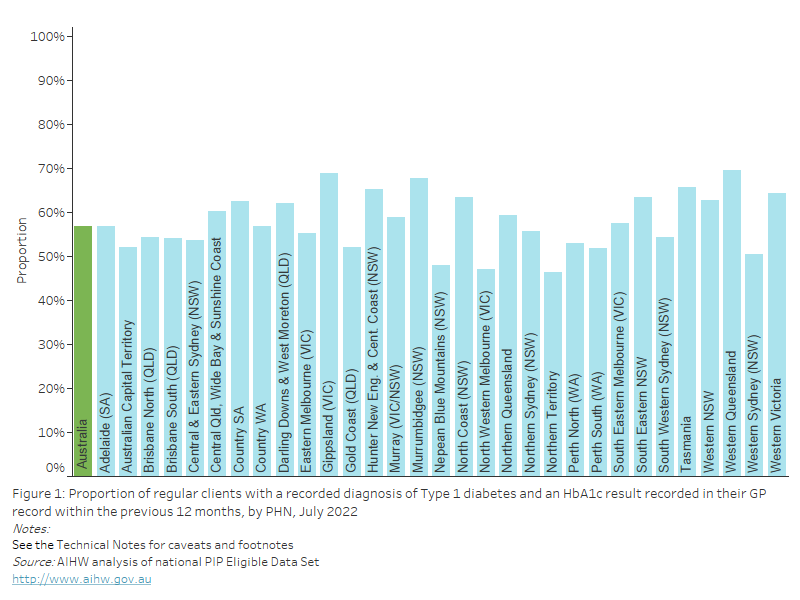
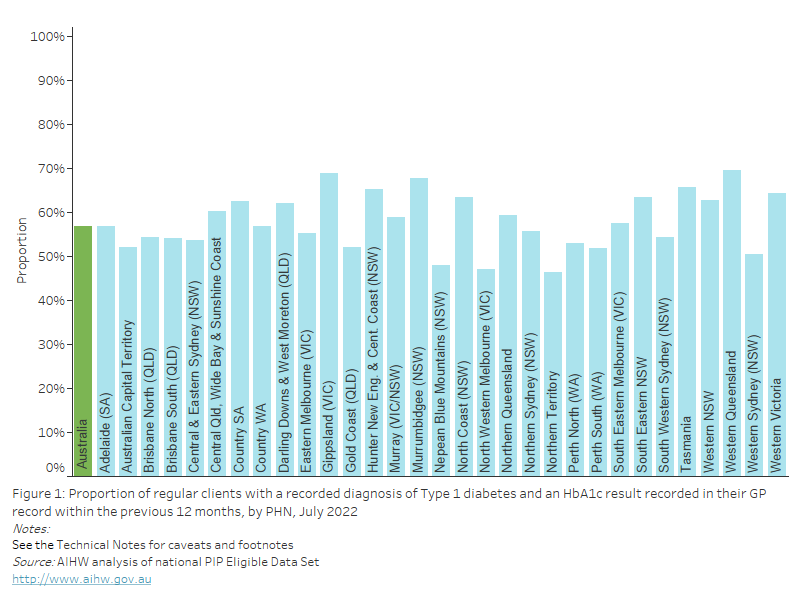
As of July 2022, nationally, 21.1% of regular clients aged 15 years and over had their height and weight measurements recorded in their GP record within the previous 12 months. This varied from 14.8 to 43.8% across PHNs.
Figure 18: Proportion of regular clients aged 15 years and over who had their height and weight measurements recorded in their GP record within the previous 12 months, by PHN, July 2022
This bar chart shows the proportion of regular clients aged 15 years and over with height and weight recorded in their GP record, by PHN for July 2022.
For clients aged 15–24 years, the BMI is included only if both the height and weight measurement have been recorded in their GP record in the previous 12 months. For those aged 25 years and over, the BMI is included in these data if the height measurement has been recorded since the client turned 25 years of age, and if the weight measurement has also been recorded in the GP record within the previous 12 months.
QIM 3a: National proportions over time
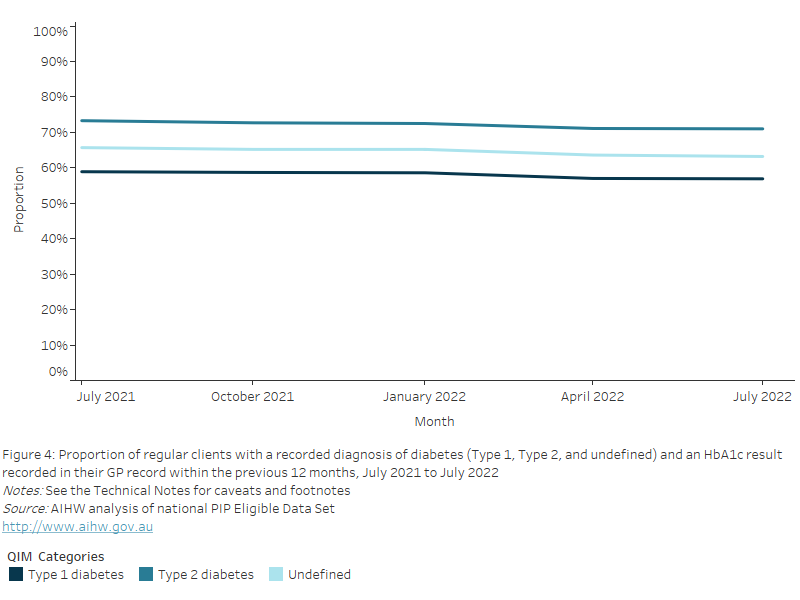
Nationally, between July 2021 and July 2022, the proportion of regular clients aged 15 years and over with a height and weight recorded in their GP record within the previous 12 months decreased by 2.5% from 23.6% to 21.1%.
Figure 19: Proportion of regular clients aged 15 years and over who had their height and weight recorded in their GP record within the previous 12 months, July 2021 to July 2022
This line chart shows the proportion of regular clients aged 15 years and over with height and weight recorded in their GP record, from July 2021 to July 2022.
QIM 3a: National proportions by age and sex
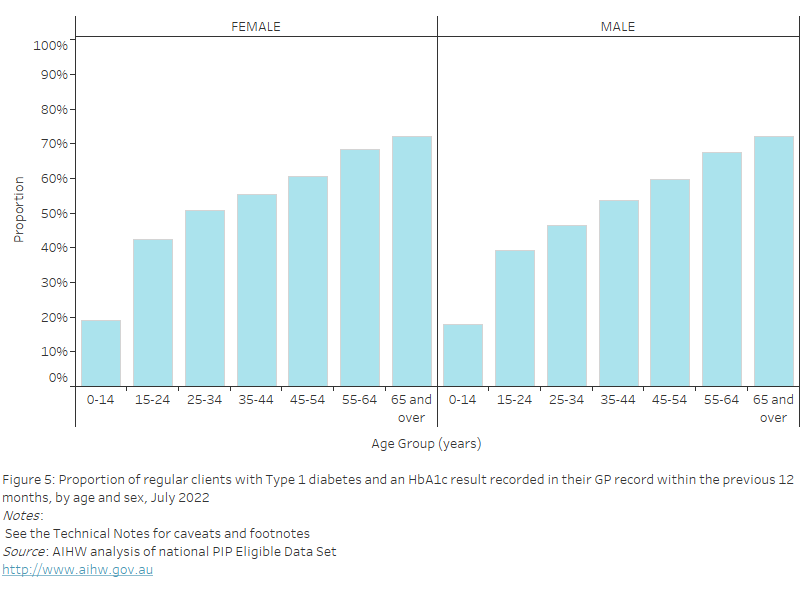
As of July 2022, nationally, the proportion of regular clients who had their height and weight recorded in their GP record in the previous 12 months increased with age and was:
- highest in the 65 years and over age group for both females (30.4%) and males (30.7%)
- lowest in the 15–24 years age group for both females (14.0%) and males (9.2%), noting the different requirement for this age group that both height and weight be recorded in the previous 12 months.
Figure 20: Proportion of regular clients aged 15 years and over who had their height and weight recorded in their GP record within the previous 12 months, by age and sex, July 2022
This bar chart shows the proportion of regular clients aged 15 years and over with height and weight recorded in their GP record, by age and sex for July 2022.
Proportion of regular clients with a weight classification result (QIM 3b)
QIM 3b: Regional Proportions
Underweight BMI
As of July 2022, nationally, 2.1% of regular clients aged 15 years and over who had their height and weight recorded in their GP record in the previous 12 months were classified as having a BMI within the underweight range. This varied from 1.4% to 2.9% across PHNs.
Figure 21: Proportion of regular clients aged 15 years and over who had their height and weight recorded in their GP record within the previous 12 months, with a BMI classification of "underweight", by PHN, July 2022
This bar chart shows the proportion of regular clients aged 15 years and over with a BMI classification of “underweight”, by PHN for July 2022.
Healthy BMI
As of July 2022, nationally, 25.3% of those regular clients aged 15 years and over who had their height and weight recorded in their GP record in the previous 12 months were classified as having a BMI within the healthy range. This varied from 18.9% to 35.4% across PHNs.
Figure 22: Proportion of regular clients aged 15 years and over who had their height and weight recorded in their GP record within the previous 12 months, with a BMI classification of "healthy", by PHN, July 2022
This bar chart shows the proportion of regular clients aged 15 years and over with a BMI classification of “healthy”, by PHN for July 2022.
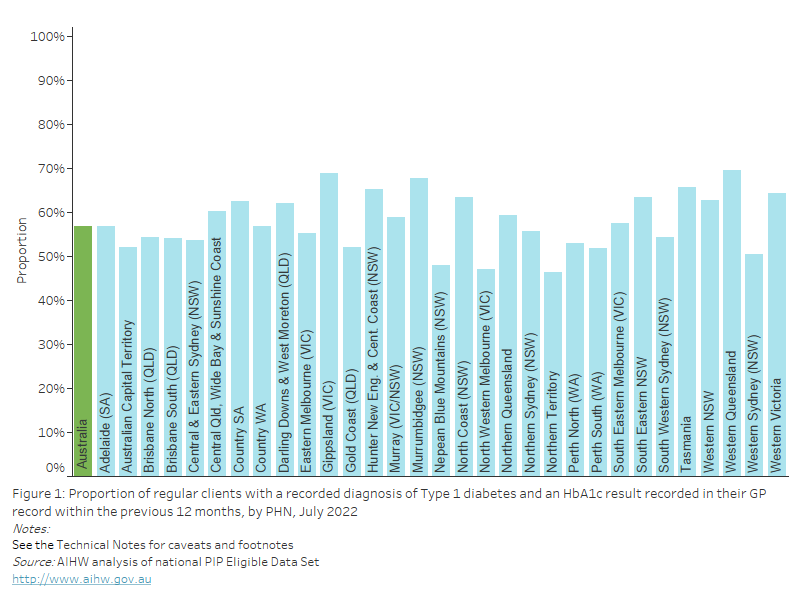
Overweight BMI
As of July 2022, nationally, 32.2% of regular clients aged 15 years and over who had their height and weight recorded in their GP record in the previous 12 months were classified as having a BMI within the overweight range. This varied from 29.0% to 34.9% across PHNs.
Figure 23: Proportion of regular clients aged 15 years and over who had their height and weight recorded in their GP record in the previous 12 months, with a BMI classification of "overweight", by PHN, July 2022
This bar chart shows the proportion of regular clients aged 15 years and over with a BMI classification of “overweight”, by PHN for July 2022.
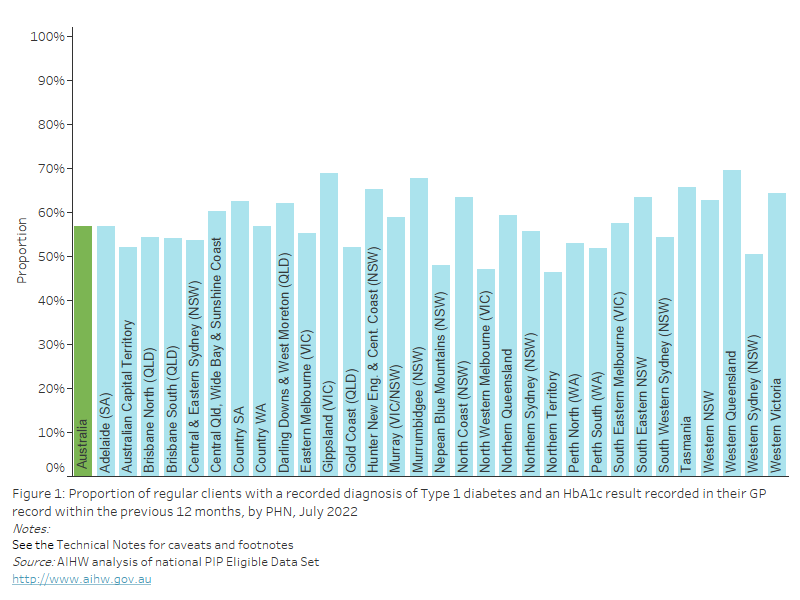
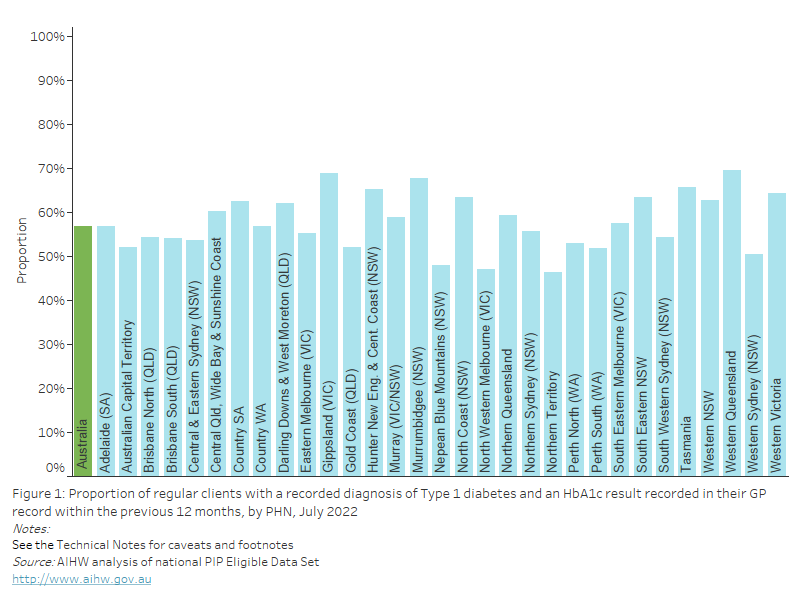
Obese BMI
As of July 2022, nationally, 40.4% of regular clients aged 15 years and over who had their height and weight recorded in their GP record in the previous 12 months were classified as having a BMI within the obese range. This varied from 26.8% to 50.3% across PHNs.
Figure 24: Proportion of regular clients aged 15 years and over who had their height and weight recorded in their GP record within the previous 12 months, with a BMI classification of "obese", by PHN, July 2022
This bar chart shows the proportion of regular clients aged 15 years and over with a BMI classification of “obese”, by PHN for July 2022.
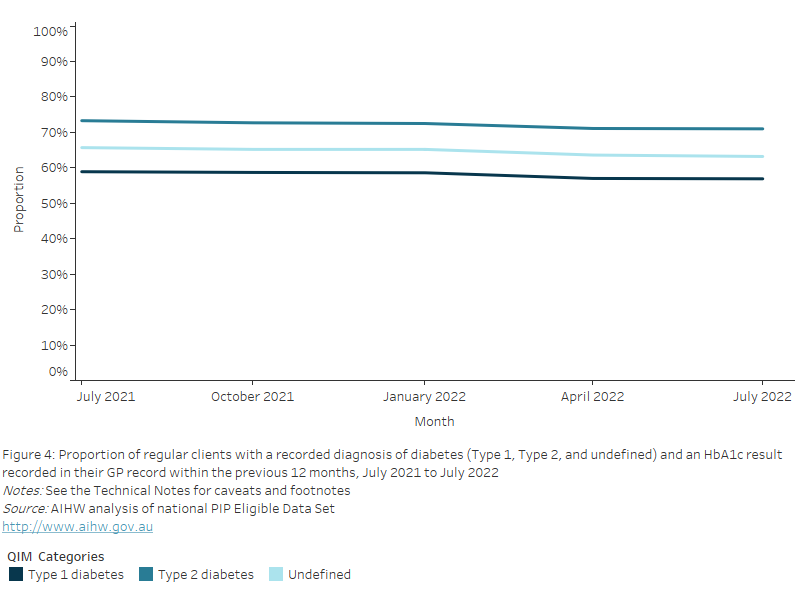
QIM 3b: National proportions over time
Nationally, between July 2021 and July 2022, of those who had their height and weight recorded in their GP record within the previous 12 months:
- a BMI status of “underweight” remained constant at 2.0% and 2.1% respectively
- a BMI status of “healthy” remained constant at 25.7% and 25.3% respectively
- a BMI status of “overweight” remained constant at 32.5% and 32.2% respectively
- a BMI status of “obese” remained constant at 39.8% and 40.4% respectively.
Figure 25: Proportion of regular clients aged 15 years and over who had their height and weight recorded in their GP record within the previous 12 months, by BMI classification, July 2021 to July 2022
This line chart shows the proportion of regular clients aged 15 years and over with a BMI classification (“underweight”, “healthy”, “overweight”, “obese"), from July 2021 to July 2022.
QIM 3b: National proportions by age and sex
Underweight BMI
As of July 2022, nationally, the proportion of regular clients with their height and weight recorded in their GP record in the previous 12 months who were classified as having a BMI in the underweight range was:
- highest in the 15–24 years age group for both females (9.1%) and males (7.8%)
- lowest in the 45–54 years age group for females (1.4%)
- lowest in the 35–44 years and 45–54 years age groups for males (0.5%).
Figure 26: Proportion of regular clients aged 15 years and over who had their height and weight recorded in their GP record within the previous 12 months, with a BMI classification of "underweight", by age and sex, July 2022
This bar chart shows the proportion of regular clients aged 15 years and over with a BMI classification of “underweight”, by age and sex for July 2022.
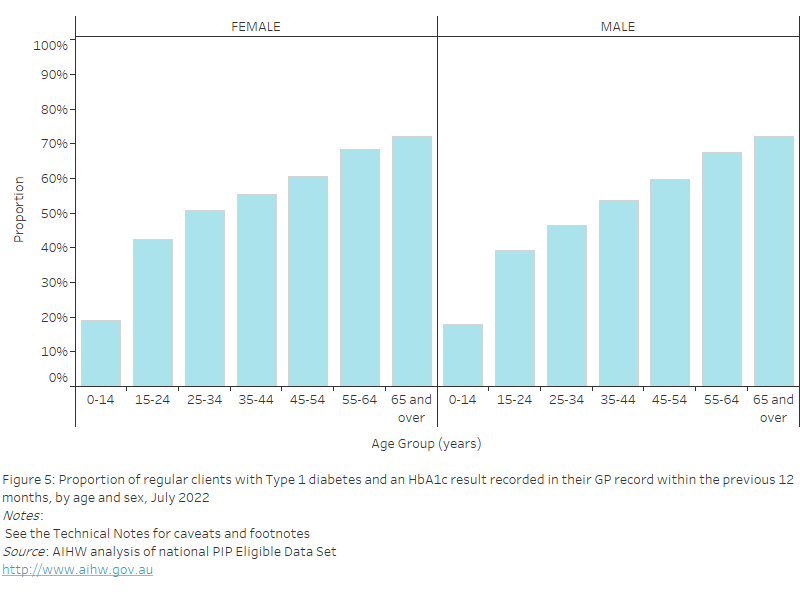
Healthy BMI
As of July 2022, nationally, the proportion of regular clients with their height and weight recorded in their GP record in the previous 12 months who were classified as having a BMI in the healthy range was:
- highest in the 15–24 years age group for both females (46.4%) and males (46.2%)
- lowest in the 45–54 years age group for both females (23.0%) and males (15.3%).
Figure 27: Proportion of regular clients aged 15 years and over who had their height and weight recorded in their GP record within the previous 12 months, with a BMI classification of "healthy", by age and sex, July 2022
This bar chart shows the proportion of regular clients aged 15 years and over with a BMI classification of “healthy”, by age and sex for July 2022.
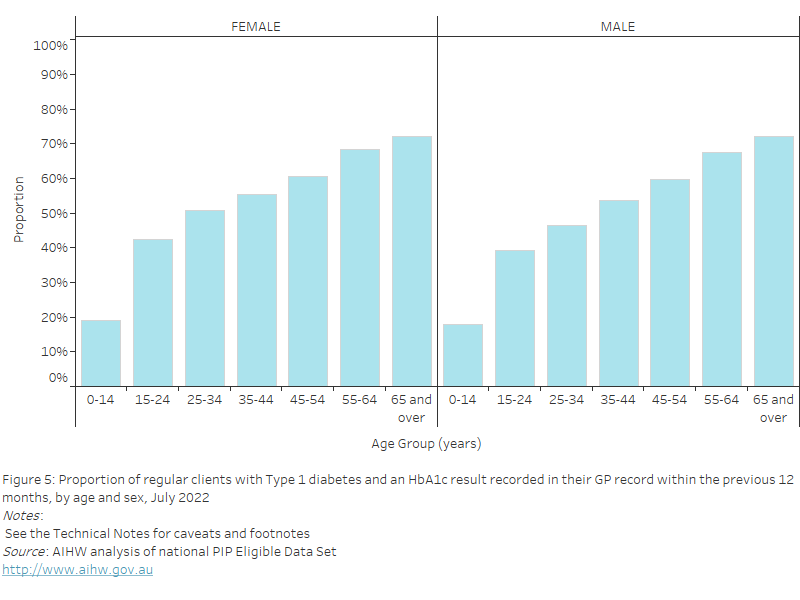
Overweight BMI
As of July 2022, nationally, the proportion of regular clients with their height and weight recorded in their GP record in the previous 12 months who were classified as having a BMI in the overweight range was:
- highest in the 65 years and over age group for both females (32.3%) and males (41.1%)
- lowest in the 15–24 years age group for both females (19.9%) and males (22.4%).
Figure 28: Proportion of regular clients aged 15 years and over who had their height and weight recorded in their GP record within the previous 12 months, with a BMI classification of "overweight", by age and sex, July 2022
This bar chart shows the proportion of regular clients aged 15 years and over with a BMI classification of “overweight”, by age and sex for July 2022.
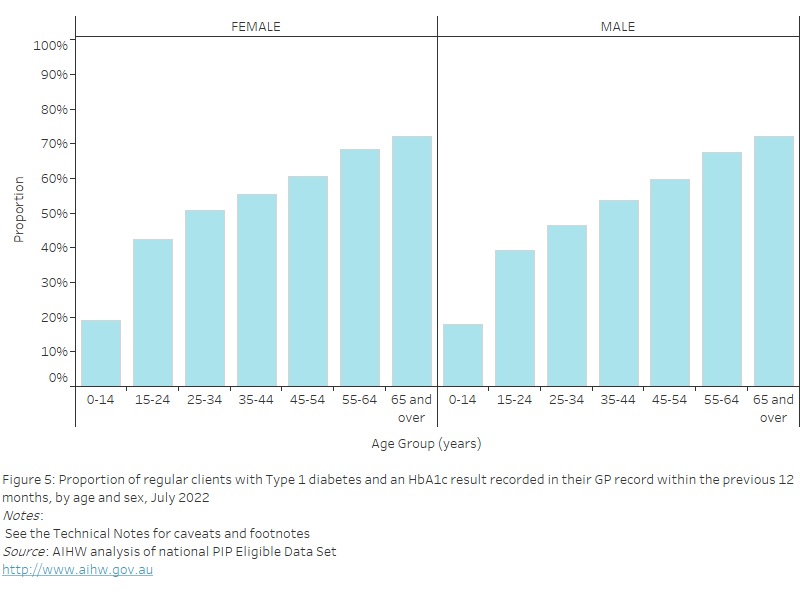
Obese BMI
As of July 2022, nationally, the proportion of regular clients with their height and weight recorded in their GP record in the previous 12 months who were classified as having a BMI in the obese range was:
- highest in the 45–54 years age group for both females (47.7%) and males (48.1%)
- lowest in the 15–24 years age group for both females (24.6%) and males (23.7%).
Figure 29: Proportion of regular clients aged 15 years and over who had their height and weight recorded in their GP record within the previous 12 months, with a BMI classification of "obese", by age and sex, July 2022
This bar chart shows the proportion of regular clients aged 15 years and over with a BMI classification of “obese”, by age and sex for July 2022.

QIM 03a: Proportion of regular client with a height and weight measurement record
- Clients aged between 15 and 24.999 years are included if both the height and weight measurement have been recorded in the previous 12 months.
- Clients aged 25 years and over are included if height has been recorded since the client turned 25 years of age and a weight has been recorded within the previous 12 months.
- Results arising from measurements conducted outside of the service that are known and recorded by the service are included in the measure.
QIM 03b: Proportion of regular clients with a derived BMI result
- Includes only those clients with a record of weight classification derived from a record of height and weight as defined in the numerator of QIM 03a.
- If the client had their BMI recorded more than once within the previous 12 months, only the most recently recorded result is included in this measure.
- Clients are excluded from the measure if they are 18 or older and either shorter than 0.914 or taller than 2.108 metres; or refused measurement.
- AIHW has been working with all vendors towards a consistent approach to the data specification interpretation, ensuring all interpretations are consistent. Due to the uneven exclusion criteria across QIM 03a and QIM 03b, not all extraction vendors excluded very tall or very short people from QIM 03b in line with the technical specifications.
- From January 2022 onwards, 27 PHNs using CAT4 re-submitted data which resolved these data inconsistencies with QIM 03.
ABS (Australian Bureau of Statistics) (2021). National Health Survey: first results, 2020-21, ABS cat. no. 4364.0.00.001, ABS, Canberra, accessed 15 August 2022.


