QIM 5: Proportion of regular clients with diabetes with an influenza immunisation status recorded in their GP record within the previous 15 months
Influenza is a common disease of the respiratory tract. It affects people of all ages. It is estimated that influenza is likely to be associated with more than 3,000 deaths and 13,500 hospitalisations each year in Australia, just in people aged >50 years (ATAGI 2018).
There are a number of groups who are at a higher risk of influenza and its complications. These groups experience higher illness and death associated with influenza than the rest of the population and patients with diabetes is one of the vulnerable population groups. Therefore, annual influenza vaccination is strongly recommended for patients with diabetes (ATAGI 2018).
While best practice guidelines recommend annual immunisation, a 15-month interval allows for cases when a client decides to receive a vaccine earlier than recommended (for example, from a pharmacy), or delay and wait for the release of an ‘enhanced’ vaccine (Department of Health 2020b).
Capture of results recorded outside of the general practice setting
Some patients may receive care from other practitioners in addition to a GP, including an endocrinologist/a specialist physician, and/or other health care providers to safely manage their diabetes (RACGP 2020b). Results arising from clinical intervention conducted outside of the service that are known and recorded by the practice are included in the measure. Where immunisation was provided elsewhere but is not known to the practice, this is not captured in the report. For example, this might be where the vaccination providers’ information systems may not be compatible with the clinical information system of the client’s usual general practice.
Other sources of relevant data
Data on the prevalence of long-term health conditions like diabetes are captured in the National Health Survey (NHS) conducted by the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS). There are other administrative data collections where the data from these client-provider interactions are captured, for example, Medicare Benefits Schedule (MBS), the National Diabetes Service Scheme (NDSS) register and the Australasian Paediatric Endocrine Groups (APEG) state and territory registers. There are other administrative data collections where data on influenza immunisation are captured, for example, the Australian Immunisation Register (AIR).
This indicator reports on the proportion of regular clients with Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes, or an undefined diabetes diagnosis, hereafter described as diabetes, who had an influenza immunisation status recorded in their GP record within the previous 15 months.
QIM 5: Regional proportions
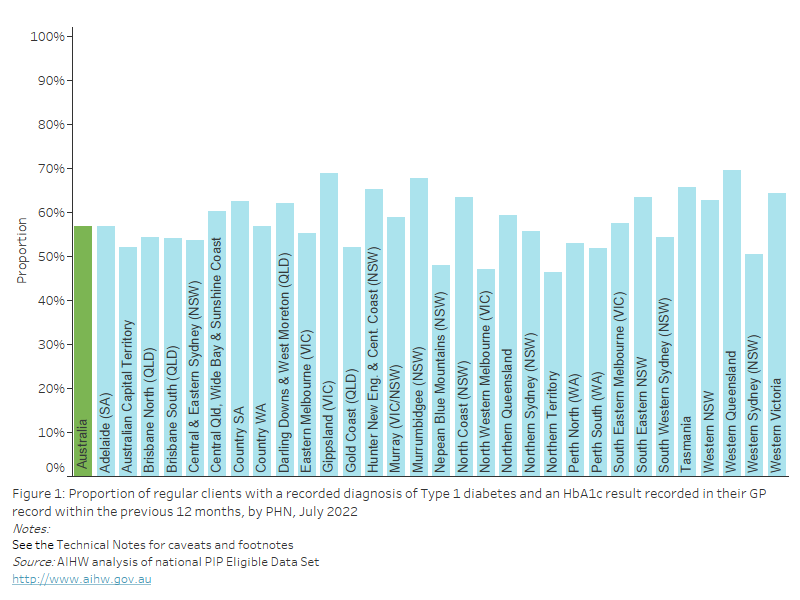
As of July 2022, nationally, 54.0% of regular clients with diabetes had an influenza immunisation status recorded in their GP record within the previous 15 months. This varied from 37.8% to 65.4% across PHNs.
Figure 33: Proportion of regular clients with diabetes (Type 1, Type 2, undefined) with an influenza immunisation status recorded in their GP record within the previous 15 months, by PHN, July 2022
This bar chart shows the proportion of regular clients with a recorded diagnosis of diabetes (Type 1, Type 2 and undefined) and an influenza immunisation status recorded in their GP record, by PHN for July 2022.
QIM 5: National proportions over time
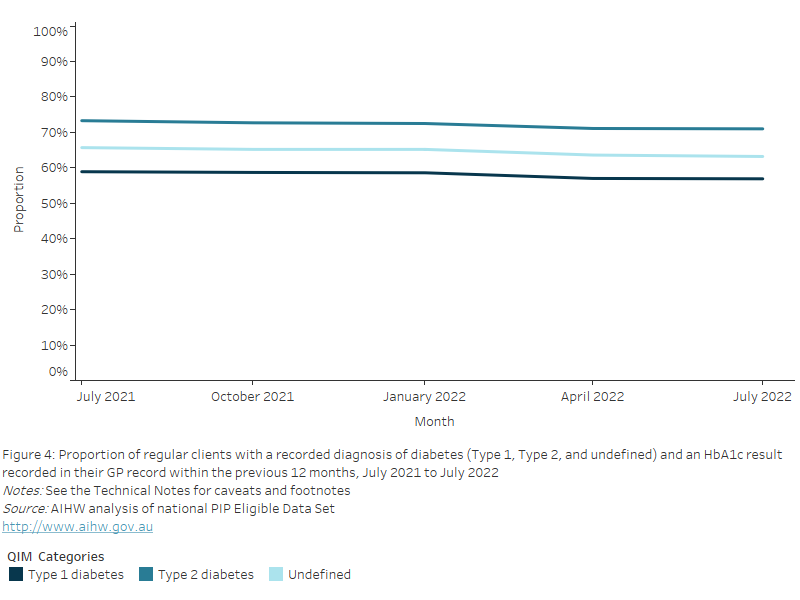
Nationally, between July 2021 and July 2022, the proportion of regular clients with Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes, or an undefined diabetes diagnosis, who had an influenza immunisation status recorded in their GP record within the previous 15 months decreased by 3.6%, from 57.6% to 54.0%.
Figure 34: Proportion of regular clients with diabetes (Type 1, Type 2, undefined) with an immunisation status recorded in their GP record within the previous 15 months, July 2021 to July 2022
This line chart shows the proportion of regular clients with a recorded diagnosis of diabetes (Type 1, Type 2 and undefined) and an influenza immunisation status recorded in their GP record, from July 2021 to July 2022.
QIM 5: National proportions by age and sex
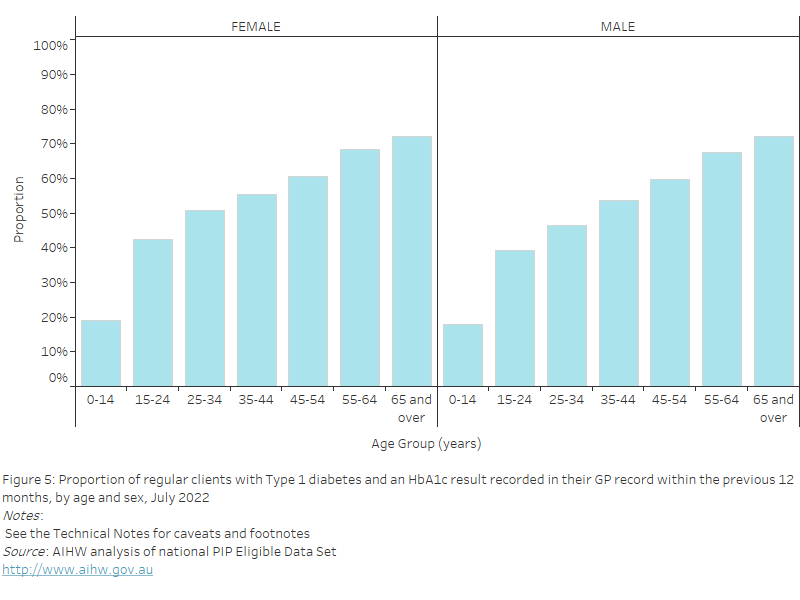
As of July 2022, nationally, the proportion of regular clients with Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes, or an undefined diabetes diagnosis, who had an influenza immunisation status recorded in their GP record within the previous 15 months was:
- highest in the 65 years and over age group for both females (69.3%) and males (68.6%)
- lowest in the 25–34 years age group for both females (24.4%) and males (18.0%).
Figure 35: Proportion of regular clients with diabetes (Type 1, Type 2, undefined) with an influenza immunisation status recorded in their GP record within the previous 15 months, by age and sex, July 2022
This bar chart shows the proportion of regular clients with a recorded diagnosis of diabetes (Type 1, Type 2 and undefined) and an influenza immunisation status recorded in their GP record, by age and sex for July 2022.
- Data for clients with diabetes are included if they have received an influenza vaccine within the previous 15 months.
- Clinical definitions for diabetes vary across clinical information systems, as different coding schemes are used. This may lead to some variation in the number of clients who will be picked up by different systems (Department of Health 2017).
- Results arising from clinical intervention conducted outside of the service that are known and recorded by the service are included in the measure. Where immunisation was given elsewhere (for example, workplace or pharmacy) and the information is not recorded in the electronic record of the client’s usual general practice, then this may result in an apparent missing information.
- A client is classified as having diabetes, if they have Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes, or a diagnosis which indicates diabetes but does not specify between Type 1 or Type 2, listed as a diagnosis in their GP record. If a client had gestational diabetes but also has Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes, they are included in the measure.
- Clients are excluded from the measure if they:
- did not have the immunisation due to documented medical reasons (e.g. allergy), system reasons (vaccine not available) or client reasons (e.g. refusal),
- had secondary diabetes, gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM), previous GDM, impaired fasting glucose, impaired glucose tolerance,
- had results from measurements conducted outside of the service which were not available to the service.
- There are other administrative data collections where the data on influenza immunisation are captured for example, the Australian Immunisation Register (AIR).
- There was a change in the recording of influenza immunisations identified in January 2022 that resulted in an undercount of the number of regular clients receiving influenza immunisations and a lower proportion reported for this QIM (Pen CS 2022). This change impacted the January 2022 and April 2022 data submissions for selected practices in 27 of the 31 PHNs.
ATAGI (Australian Technical Advisory Group on Immunisation) (2018). Australian Immunisation Handbook, Australian Government Department of Health, Canberra, accessed 15 August 2022.
Department of Health (2020b). Practice Incentives Program Quality Improvement Measures User Guide for General Practices, Department of Health, Canberra, accessed 12 August 2022.
Department of Health (2017) National Key Performance Indicators for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander primary health care, Department of Health, Canberra, accessed 12 August 2022.
Pen CS (2022) CAT4 Release Notes v4.39 January 2022, accessed 15 August 2022.
RACGP (2020b). Management of type 2 diabetes: A handbook for general practice, RACGP, East Melbourne, Victoria, accessed 12 August 2022.


