Profile of First Nations people
Citation
AIHW
Australian Institute of Health and Welfare (2023) Profile of First Nations people, AIHW, Australian Government, accessed 26 April 2024.
APA
Australian Institute of Health and Welfare. (2023). Profile of First Nations people. Retrieved from https://www.aihw.gov.au/reports/australias-welfare/profile-of-indigenous-australians
MLA
Profile of First Nations people. Australian Institute of Health and Welfare, 07 September 2023, https://www.aihw.gov.au/reports/australias-welfare/profile-of-indigenous-australians
Vancouver
Australian Institute of Health and Welfare. Profile of First Nations people [Internet]. Canberra: Australian Institute of Health and Welfare, 2023 [cited 2024 Apr. 26]. Available from: https://www.aihw.gov.au/reports/australias-welfare/profile-of-indigenous-australians
Harvard
Australian Institute of Health and Welfare (AIHW) 2023, Profile of First Nations people, viewed 26 April 2024, https://www.aihw.gov.au/reports/australias-welfare/profile-of-indigenous-australians
Get citations as an Endnote file: Endnote

On this page:
Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander (First Nations) people are the first peoples of Australia. They are not one group, but rather comprise hundreds of groups that have their own distinct set of languages, histories and cultural traditions (AIHW 2015). The health and welfare of First Nations people living in the big cities are different to those living in the Torres Strait, which are different again to those living on the outskirts of Alice Springs or those living in remote communities.
This page provides demographic information on the First Nations population, including information on their languages and cultures. Information is also included on the Closing the Gap targets.
First Nations identification in data collections
In most Australian data collections, First Nations people refers to people who have identified themselves, or have been identified by a representative (for example, their parent or guardian), as being of Aboriginal and/or Torres Strait Islander origin. For a few data collections, such as those associated with government grants and payments, information on acceptance of a person as being First Nations by a First Nations community may also be required.
Colonisation is recognised as having a fundamental impact on the disadvantage and poor health of First Nations peoples worldwide, through social systems that maintain disparities (see, for example, Thurber et al. 2022; Paradies 2016; Paradies and Cunningham 2012). In Australia, the historical and ongoing effects of colonisation and racism have contributed, at least in large part, to current inequities in the health and wellbeing of First Nations people. In contrast, cultural factors – such as connection to Country and caring for Country, knowledge and beliefs, language, self-determination, family and kinship, and cultural expression – can be protective and positively influence First Nations people's health and wellbeing (see, for example, Thurber et al. 2022; Bourke et al. 2018).
Population size and location
As of 30 June 2021, preliminary Australian Bureau of Statistics' (ABS) estimates indicate that 984,000 First Nations people were living in Australia, representing 3.8% of the total Australian population. This was an increase of 23% (185,600 people) from the 30 June 2016 estimate of 798,400 (ABS 2018, 2022b).
The proportion of First Nations people has increased each Census of Population and Housing (the Census) since 2001 – from 2.4% in 2001, to 2.5% in 2006, 3.0% in 2011, 3.3% in 2016, and 3.8% in 2021 (Figure 1). This increase is not completely explained by demographic factors. Other factors, such as changing identification in the Census and throughout life, an undercount for ages 0–4 in the 2016 Census, greater participation in the 2021 Census and a higher response rate to the question on Indigenous status, have also contributed to changes in counts of First Nations people (ABS 2023).
Figure 1: Proportion of First Nations people in the Census, 2001 to 2021
This figure shows that the estimated proportion of First Nations people has increased from 2.4% in 2001, to 2.5% in 2006, 3.0% in 2011, 3.3% in 2016, and 3.8% in 2021.
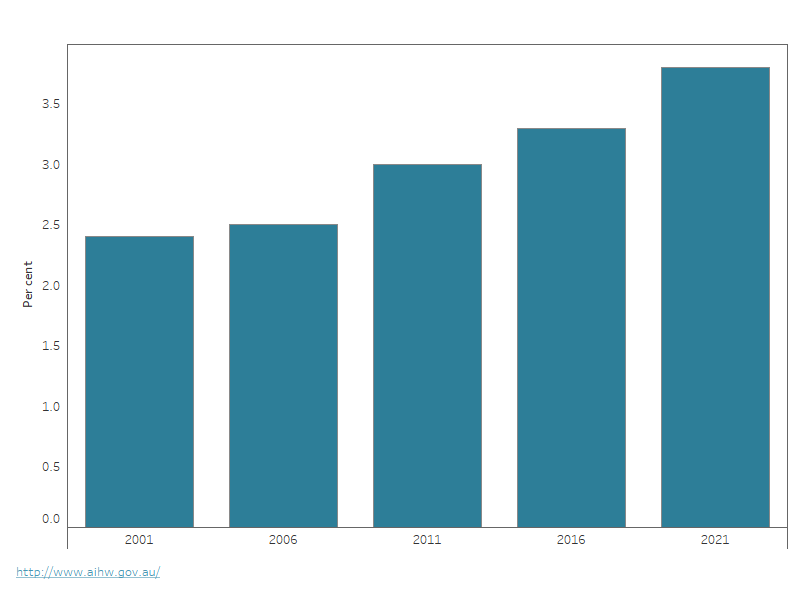
Note: Data are ABS Census-based estimated resident population (final estimates for 2001 to 2016 and preliminary estimates for 2021).
Sources: ABS 2003, 2008, 2013, 2018, 2022b.
Based on 2021 Census counts of First Nations population (around 812,700 people):
- 91.4% identified as being of Aboriginal origin
- 4.2% identified as being of Torres Strait Islander origin
- 4.4% identified as both Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander (ABS 2022a).
About First Nations populations estimates
The ABS produces Estimated Resident Populations (ERPs) for First Nations people every 5 years (the Census years).
The 2021 estimates of First Nations population on this page are from the ABS preliminary 2021 Census-based estimated resident population of First Nations and non-Indigenous Australians. Final estimates will be released 31 August 2023. See Estimates of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Australians.
The ABS also produces ‘back cast estimates’ for years before the latest Census year and ‘projections’ for future years, based on the latest Census year estimates along with assumptions about births, deaths and migration (see Estimates and Projections, Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Australians for details). The latest available projections are based on the 2016 Census. The 2016 Census-based projections, first published by the ABS in 2019, do not account for any impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic. See Estimates and Projections, Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Australians and Estimates of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Australians for details.
Age distribution
The First Nations population has a relatively young age structure, with larger proportions of people aged 29 and under, when compared with the non-Indigenous population. As of 30 June 2021, an estimated one-third (33%) of the First Nations population was aged under 15, compared with 18% of non-Indigenous people in the same age group (ABS 2022a; Figure 2). The median age of First Nations people has increased – from 21 in 2011, to 23 in 2016 and 24 in 2021 (ABS 2022b).
Figure 2: First Nations population by age and sex, 30 June 2021
This figure shows the distribution of the estimated First Nations population by age and sex. It shows the relatively young age profile of First Nations people, with 33% aged under 15.
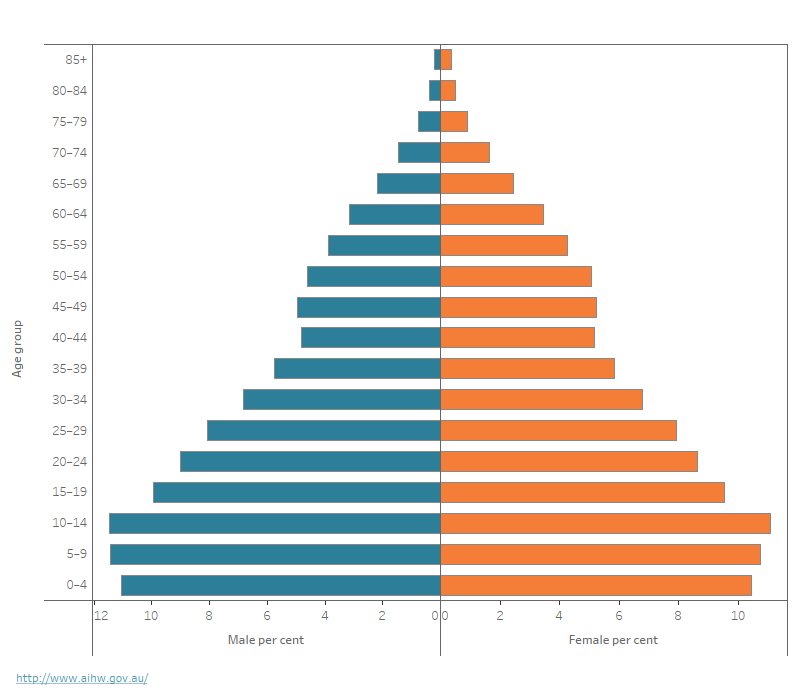
Note: Data are ABS 2021 Census-based estimated resident population (preliminary estimates).
Source: ABS 2022b.
Geographic distribution
First Nations people are more likely to live in urban and regional areas than remote areas, though the proportion of the total population who are First Nations is generally higher in more remote areas.
Based on 2016 Census-based projections, in 2023, among First Nations people:
- 39% (353,300) live in Major cities
- 44% (404,000) live in Inner and outer regional areas
- 17% (156,600) live in Remote and very remote areas combined (Figure 3; ABS 2019).
The proportion of the total population who were First Nations increased with remoteness, from 1.9% in Major cities, to 32% in Remote and very remote areas.
In 2023, a projected 33% of First Nations people (303,200 people) live in New South Wales and 28% (258,400 people) in Queensland (Figure 3).
The Northern Territory has the highest proportion of First Nations residents among its population – a projected 30% (79,700 people) (Figure 3).
Figure 3: First Nations population by geography, 2023
The figure shows that the majority (33.2%) of First Nations people live in New South Wales, followed by Queensland (28.3%) and Western Australia (12.5%). The Australian Capital Territory has the smallest proportion of Australia’s First Nations population (1.0%).
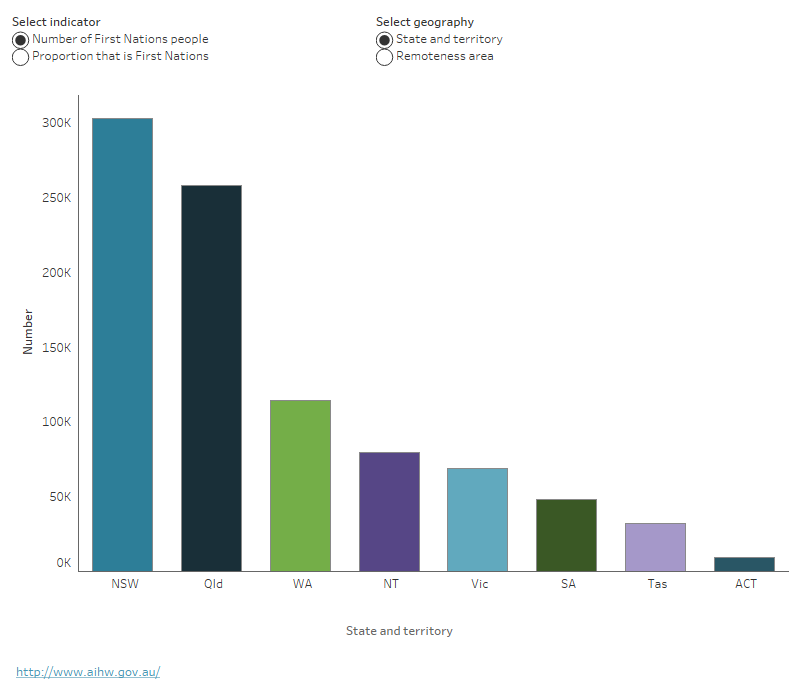
Notes
- 'Proportion that is First Nations' by remoteness is calculated using ABS 2016 Census-based projections for 2021 as the denominator.
- All other data are ABS 2016 Census-based projections for 2023 (Series B).
Source: ABS 2019.
Language and culture
First Nations communities pass on knowledge, tradition, ceremony and culture from one generation to the next through language, performance, protection of significant sites, storytelling and the teachings of Elders. Cultural factors, such as connection to community, land and spirituality, are important for the social and emotional wellbeing of First Nations people (Bourke et al. 2018).
In the 2021 Census, almost 1 in 10 (9.5% or around 77,000) First Nations people reported that they spoke a First Nations language at home, with over 150 different First Nations languages being spoken. The Australian Standard Classification of Languages (ASCL) used for the Census does not list all languages spoken and, in order to be separately identified, a First Nations language must have 3 or more known speakers. Where responses to the Census question on language cannot be coded to a finer level or where there are not enough speakers of a language for it to be given a separate code, supplementary codes of 'nes' and 'nec' are used, respectively.
In 2021, the most common First Nations languages spoken at home were Yumplatok (Torres Strait Creole) (around 7,600 or 9.9% of First Nations people who spoke a First Nations language at home) and Kriol (around 7,400 people or 9.6%) (ABS 2022c; Figure 4). These were also the most commonly spoken languages in 2016 (ABS 2022c).
Yumplatok (Torres Strait Creole) and Kriol
During colonisation, speaking traditional languages was generally discouraged. This resulted in some languages being lost or merging with other languages to form new languages. Yumplatok and Kriol are both recently developed English-based creole languages (that is, these languages are a mixture of Standard Australian English and traditional languages). Yumplatok, in particular, is a common language shared by all Torres Strait Islanders and is often spoken in addition to other local languages.
Figure 4: Proportion of First Nations people who spoke a First Nations language at home, by language spoken, 2021
This figure shows that the most commonly spoken First Nations languages in 2021 were Yumplatok (Torres Strait Creole) (9.9%) and Kriol (9.6%).
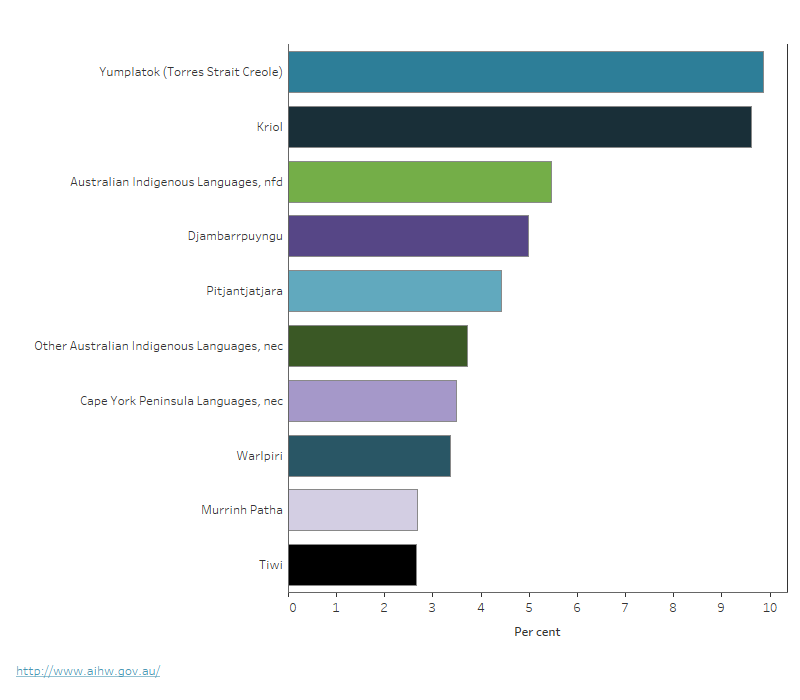
Notes
- Proportion is of First Nations people who spoke a First Nations language at home from the 2021 Census.
- ‘Australian Indigenous language, nfd’ is a supplementary code in the ASCL and is used when responses cannot be coded to a finer level.
- ‘Other Indigenous language, nec’ is used for any language which is not separately identified in the ASCL because it does not meet the threshold for the minimum number of speakers.
Source: ABS 2022c.
The proportion of First Nations people who spoke a First Nations language at home has declined over time – from 16.4% in 1991 to 9.8% in 2016 and 9.5% in 2021 (ABS 2022c).
Data from the 2018–19 National Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Health Survey show that First Nations people have strong connections to their family, community and culture. In 2018–19, among First Nations people aged 18 and over an estimated:
- 74% (357,800 people) recognised an area as a homeland/traditional country – this was 90% in remote areas compared with 71% in non-remote areas.
- 65% (314,200 people) identified with a tribal group, language, clan, mission or regional group – this was 86% in remote areas compared with 61% in non-remote areas.
- 27% (130,500 people) lived on their homeland – this was 47% in remote areas compared with 23% in non-remote areas (Figure 5; AIHW and NIAA 2020).
Figure 5: Selected measures of cultural connectedness among First Nations people aged 18 and over by remoteness, 2018–19
The figure show that, across all measures, the proportion of First Nations people who are connected to their culture is higher in remote areas.
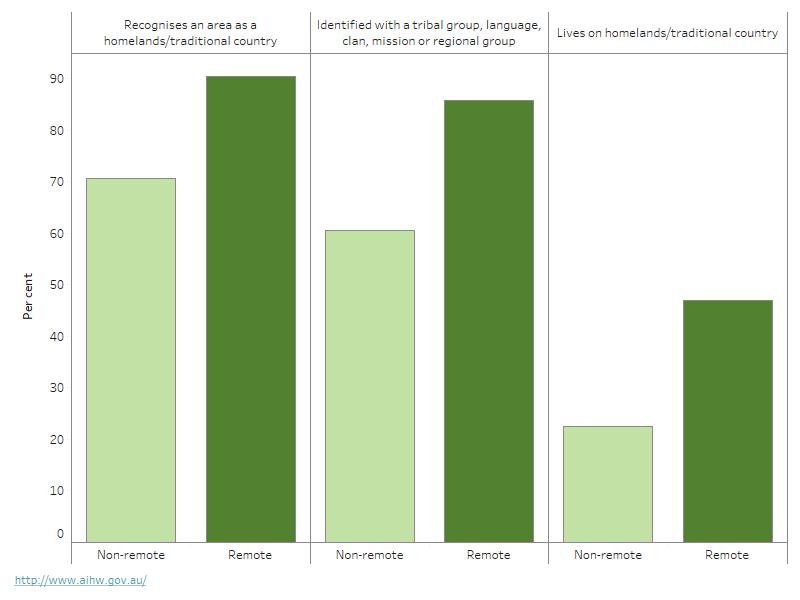
Note: Remoteness classified according to the Australian Statistical Geography standard 2016. 'Non-remote' includes Major cities, Inner regional areas and Outer regional areas. 'Remote' includes Remote and Very remote areas.
Source: AIHW and NIAA 2020.
Closing the Gap targets
Closing the Gap is a government framework aiming to reduce disadvantage among First Nations people. It was first agreed in 2008. Four of the original 7 targets expired unmet.
In 2020, there was a marked shift in the approach to the Closing the Gap framework, with the signing of a new National Agreement on Closing the Gap (National Agreement). For the first time, this agreement was developed in genuine partnership between Australian governments and the Coalition of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Peak Organisations.
The National Agreement is built around 4 Priority Reforms that focus on changing the way governments work with First Nations people. The National Agreement also identifies 17 socioeconomic outcome areas with 19 targets across these areas (Table 1).
The targets in the National Agreement are monitored annually by the Productivity Commission and reported in their Closing the Gap Information Repository Dashboard (PC 2022).
| Socioeconomic outcome area | Target |
|---|---|
| 1 | Close the Gap in life expectancy within a generation, by 2031. |
| 2 | By 2031, increase the proportion of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander babies with a healthy birthweight to 91%. |
| 3 | By 2025, increase the proportion of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander children enrolled in Year Before Fulltime Schooling (YBFS) early childhood education to 95%. |
| 4 | By 2031, increase the proportion of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander children assessed as developmentally on track in all five domains of the Australian Early Development Census (AEDC) to 55%. |
| 5 | By 2031, increase the proportion of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people (age 20–24) attaining year 12 or equivalent qualification to 96%. |
| 6 | By 2031, increase the proportion of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people aged 25–34 years who have completed a tertiary qualification (Certificate III and above) to 70%. |
| 7 | By 2031, increase the proportion of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander youth (15–24 years) who are in employment, education or training to 67%. |
| 8 | By 2031, increase the proportion of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people aged 25–64 who are employed to 62%. |
| 9 |
|
| 10 | By 2031, reduce the rate of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander adults held in incarceration by at least 15%. |
| 11 | By 2031, reduce the rate of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander young people (10–17 years) in detention by 30%. |
| 12 | By 2031, reduce the rate of over-representation of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander children in out-of-home care by 45%. |
| 13 | By 2031, the rate of all forms of family violence and abuse against Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander women and children is reduced at least by 50%, as progress towards zero. |
| 14 | Significant and sustained reduction in suicide of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people towards zero. |
| 15 |
|
| 16 | By 2031, there is a sustained increase in number and strength of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander languages being spoken. |
| 17 | By 2026, Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people have equal levels of digital inclusion. |
For more information on the Closing the Gap targets, see:
- Community safety for First Nations people
- Education of First Nations people
- Employment of First Nations people.
Indigenous COVID-19 advisory groups and response
The National Aboriginal Community Controlled Health Organisation (NACCHO), in partnership with the Australian Government, has been critical in responding to COVID-19 for First Nations people. NACCHO is the national leadership body for First Nations health in Australia. It provides advice and guidance to the Australian Government on policy and budget matters and advocates for community-developed solutions that contribute to the quality of life and improved health outcomes for First Nations people.
In March 2020, the Australian Government established the Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Advisory Group on COVID-19 (the Taskforce), co-chaired by NACCHO and the Department of Health. The Taskforce provides culturally appropriate advice to the Department of Health about health issues related to COVID-19, and developed the Management Plan for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander populations. This plan focuses on culturally appropriate testing and care for First Nations people. It supports health care professionals working with First Nations communities and peoples to develop and implement local operational plans.
After consultation with the First Nations health sector (through the Taskforce) and with state and territory governments, in March 2021, the Australian Government released the COVID-19 Vaccination Program – Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Peoples Implementation Plan. This plan builds on Australia's COVID-19 Vaccine National Rollout Strategy (released 7 January 2021) and complements the Management Plan for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander populations. Under it, vaccines were administered to First Nations people at Aboriginal Community Controlled Health Organisations, state and territory government-run Aboriginal Medical Services and other providers.
The First Nations Peoples Strategic Advisory Group (FNPSAG) was set up in 2020 to support the Disability Royal Commission in its work by providing leadership and guidance on matters specific to First Nations people with disability. Regarding COVID-19, the FNPSAG released a Statement of Concern endorsed by over 70 disability organisations in March 2020 and an issues paper on emergency planning and response in April 2020. The FNPSAG noted in their Statement of Concern that First Nations people with disability are not only disproportionally affected by the COVID-19 pandemic in general because they have an increased risk of infection and death. They are also disproportionally affected by the associated social restrictions imposed on them and the resulting breaks in the continuity of essential services (Disability Royal Commission 2020a, 2020b).
Where do I go for more information?
Visit First Nations people for more on this topic.
For more information on First Nations people, see:
- Indigenous Health Performance Framework
- Australian Bureau of Statistics Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Peoples.
For information on the Closing the Gap framework, such as the National Agreement and targets, see Closing the Gap.
For data on each Closing the Gap target by jurisdiction, see the Productivity Commission Closing the Gap Information Repository Dashboard.
ABS (Australian Bureau of Statistics) (2003) Estimates and projections, Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Australians, ABS, Australian Government, accessed 11 January 2023.
ABS (2008) Experimental Estimates of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Australians, Jun 2006, ABS website, accessed 11 January 2023.
ABS (2013) Estimates of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Australians, June 2011, ABS, Australian Government, accessed 11 January 2023.
ABS (2018) Estimates of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Australians, ABS, Australian Government, accessed 11 January 2023.
ABS (2019) Estimates and projections, Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Australians, ABS, Australian Government, accessed 20 May 2023.
ABS (2022a) Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people: Census, ABS, Australian Government, accessed 11 January 2023.
ABS (2022b) Estimates of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Australians, ABS, Australian Government, accessed 11 January 2023.
ABS (2022c) Language Statistics for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Peoples, ABS, Australian Government, accessed 11 January 2023.
ABS (2023) Understanding change in counts of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Australians: Census, ABS, Australian Government, accessed 21 April 2023.
AIHW (Australian Institute of Health and Welfare) (2015) The health and welfare of Australia’s Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples: 2015, AIHW, Australian Government, accessed 31 May 2023.
AIHW and NIAA (National Indigenous Australians Agency) (2020) 2.14 Indigenous people with access to their traditional lands, AIHW and NIAA, Australian Government, accessed 11 May 2023.
Bourke S, Wright A, Guthrie J, Russell L, Dunbar T and Lovett R (2018) ‘Evidence review of Indigenous culture for health and wellbeing’, International Journal of Health, Wellness & Society, 8(4):11-27, DOI:10.18848/2156-8960/CGP/v08i04/11-27.
Disability Royal Commission (Royal Commission into Violence, Abuse, Neglect and Exploitation of People with Disability) (2020a) Report: Public hearing 5 - Experiences of people with disability during the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, Disability Royal Commission, accessed 20 December 2020.
Disability Royal Commission (2020b) The First Nations Peoples Strategic Advisory Group, Disability Royal Commission, accessed 12 April 2021.
Paradies Y (2006) ‘A systematic review of empirical research on self-reported racism and health’, International Journal of Epidemiology, 35(4): 888–901, DOI: 10.1093/ije/dyl056.
Paradies Y (2016) ‘Colonisation, racism and indigenous health’, Journal of Population Research, 33(1): 83–96.
Paradies Y and Cunningham J (2012) ‘The DRUID study: racism and self-assessed health status in an Indigenous population’, BMC Public Health, 12:131.
Priest N, Paradies Y, Stewart P and Luke J (2011) ‘Racism and health among urban Aboriginal young people, BMC Public Health, 11:568.
PC (Productivity Commission) (2022) Closing the gap information repository: dashboard, Productivity Commission, Australian Government, accessed 8 February 2023.
Thurber KA, Brinckley MM, Jones R, Evans O, Nichols K, Priest N, Guo S, Williams DR, Gee GC, Joshy G, Banks E, Thandrayen J, Baffour B, Mohamed J, Calma T and Lovett R (2022) ‘Population-level contribution of interpersonal discrimination to psychological distress among Australian Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander adults, and to Indigenous–non-Indigenous inequities: cross-sectional analysis of a community-controlled First Nations cohort study’, The Lancet, 400(10368): 2084–2094.


