Trends in Medicare-subsidised allied health service use
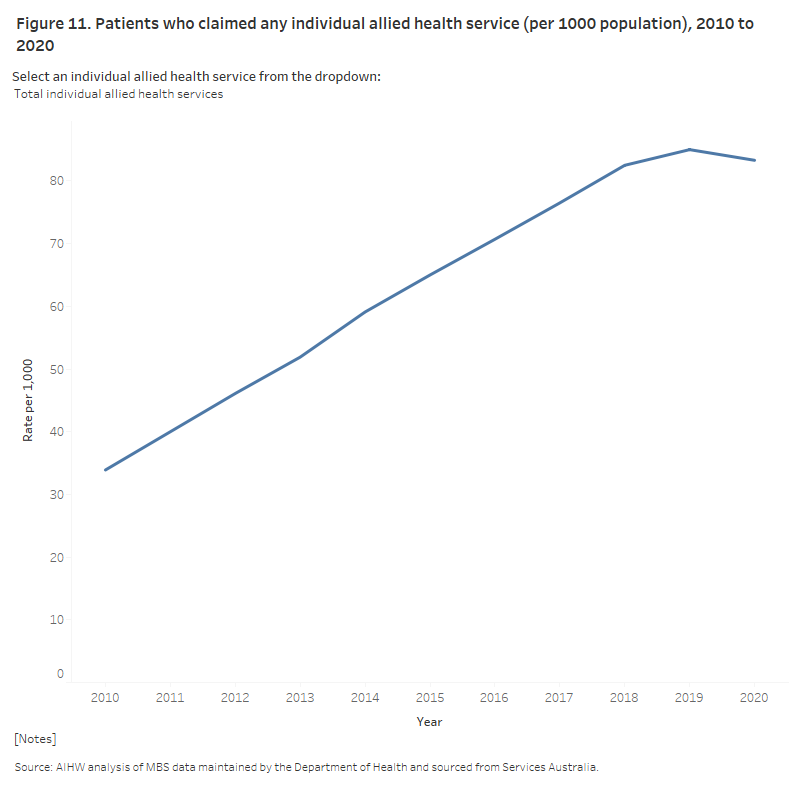
The use of Medicare-subsidised individual allied health services has increased steadily over the past decade (Figure 11). The rate of patients claiming these services more than doubled from 34 per 1,000 population in 2010 to 85 per 1,000 population in 2019 (See Data Table 2.4). The rate remained the stable between 2019 and 2020; see Impact of COVID-19 on CDM and allied health services for further analysis of 2020 activity.
Figure 11 also shows trends for selected Medicare-subsidised individual allied health services.
This bar chart shows how many patients, claimed allied health services from 2010 to 2020, and is calculated as a rate per 1000 population. The graph shows a steady increase in patients till 2019 and a slight decrease in 2020.
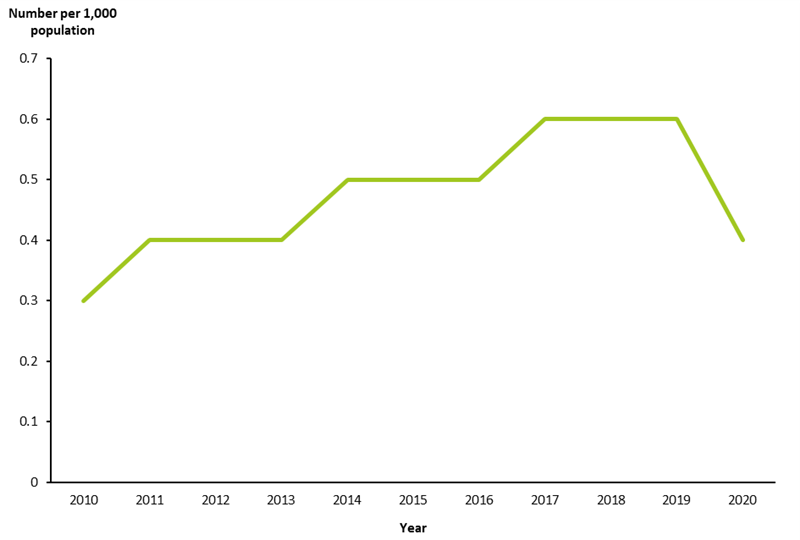
The use of group allied health services has generally increased over time from 2010 to 2019, with a degree of fluctuation (Figure 12). The rate of patients using group services dropped between 2019 and 2020; see Impact of COVID-19 on CDM and allied health services for further analysis of 2020 activity.
Figure 12: Patients who claimed group allied health services (per 1,000 population), 2010 to 2020
Notes
- Age-standardised to the 2001 Australian standard population.
- Includes MBS items: 81100, 81105, 81110, 81115, 81120, 81125.
Source: AIHW analysis of MBS data maintained by the Department of Health and Aged Care and sourced from Services Australia (Data Table 2.5).


