Procedures
Definition of procedure
A procedure is defined as a clinical intervention that:
- is surgical in nature, and/or
- carries a procedural risk, and/or
- carries an anaesthetic risk, and/or
- requires specialised training, and/or
- requires special facilities or equipment only available in an acute care setting.
– AIHW METEOR ID: 699716.
Number of procedures
Among the 23,445 patients in the cohort, there were almost 66,800 procedures administered (an average of 2.8 procedures each) during patients' initial TBI hospitalisations. However, half the patients in the cohort (11,700; 50%) did not receive any procedures (for example, where the patient only required observation). Among the 11,750 (50%) who received at least one procedure, the average number of procedures was 5.7 per patient.
The average number of procedures per patient varied by TBI diagnosis (Figure 13; Table S7). Among patients with a TBI as a principal diagnosis, patients with a concussive TBI received many fewer procedures than patients with other types of TBIs as a principal diagnosis. The same pattern occurred among patients with an additional diagnosis TBI, but those patients received more procedures on average than patients with a principal diagnosis TBI. Note, that it is not possible to say whether or to what extent procedures were for treatment of the TBI or, in the case of patients who had other non-TBI diagnoses, for other conditions.
Figure 13: Average number of procedures per cohort patient during initial TBI hospitalisation by type of TBI
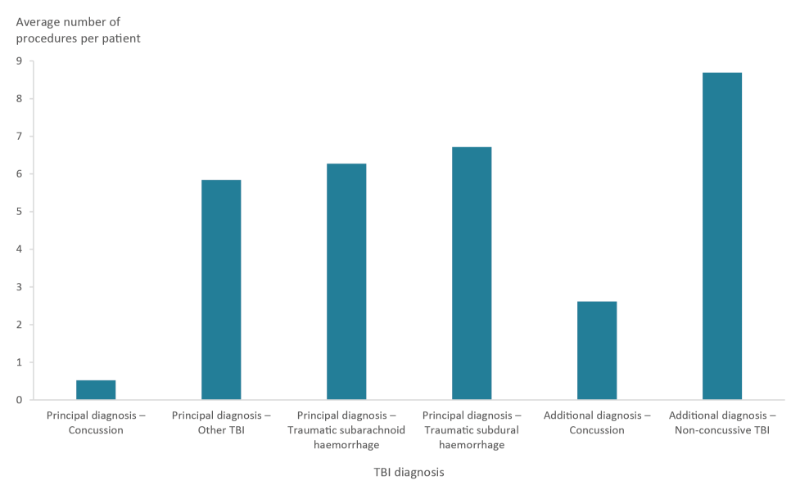
Source: AIHW NIHSI AA v0.5.
Types of procedure
Half (51%; 34,250) of procedures performed during initial TBI admissions were allied health interventions and 11.5% were for general anaesthesia or sedation (Figure 14; Table S8).
Figure 14: Most common procedures received by cohort patients during initial TBI hospitalisations
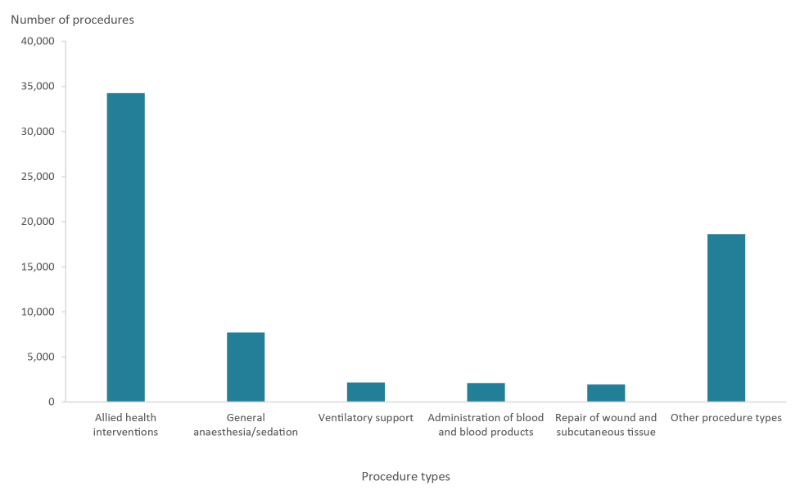
Source: AIHW NIHSI AA v0.5.
Among the 34,250 allied health interventions provided, physiotherapy was the most common procedure (14% of procedures; 9,100), followed by occupational therapy (12%; 8,200) and social work (8.3%; 5,600) (Figure 15; Table S7).
Figure 15: Most common allied health interventions provided to cohort patients during initial TBI hospitalisations
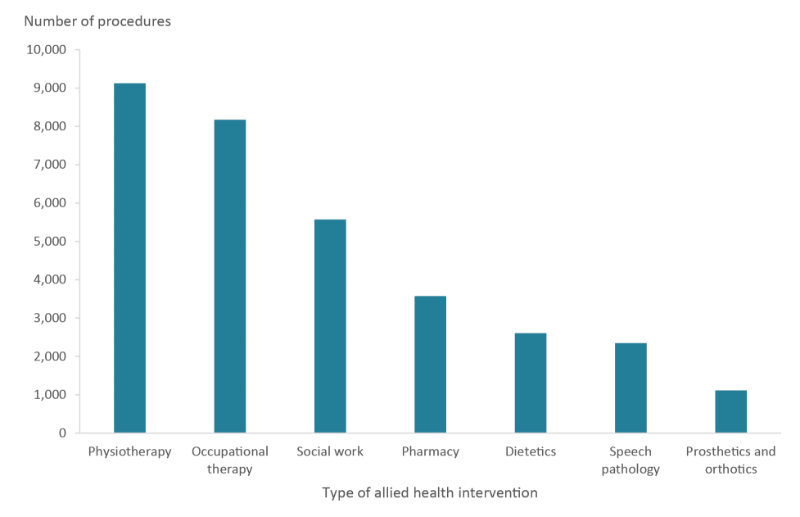
Source: AIHW NIHSI AA v0.5.


