Free sugar consumption
KPI 13: Proportion of people who regularly consume sugar sweetened beverages and/or confectionary
A healthy diet is an important factor in maintaining health and wellbeing. The Australian Dietary Guidelines, developed by the National Health and Medical Research Council, recommend limiting intake of foods containing added sugars (NHMRC 2013). The consumption of free sugars is a significant risk factor for dental caries (COAG 2019).
The available data presented here is not fully matched to the KPI that specifies consumption of sugar sweetened beverages and/or confectionary. Data presented below are self-reported from the 2017–18 National Health Survey and relate to the consumption of selected sugar sweetened drinks only (ABS 2018).
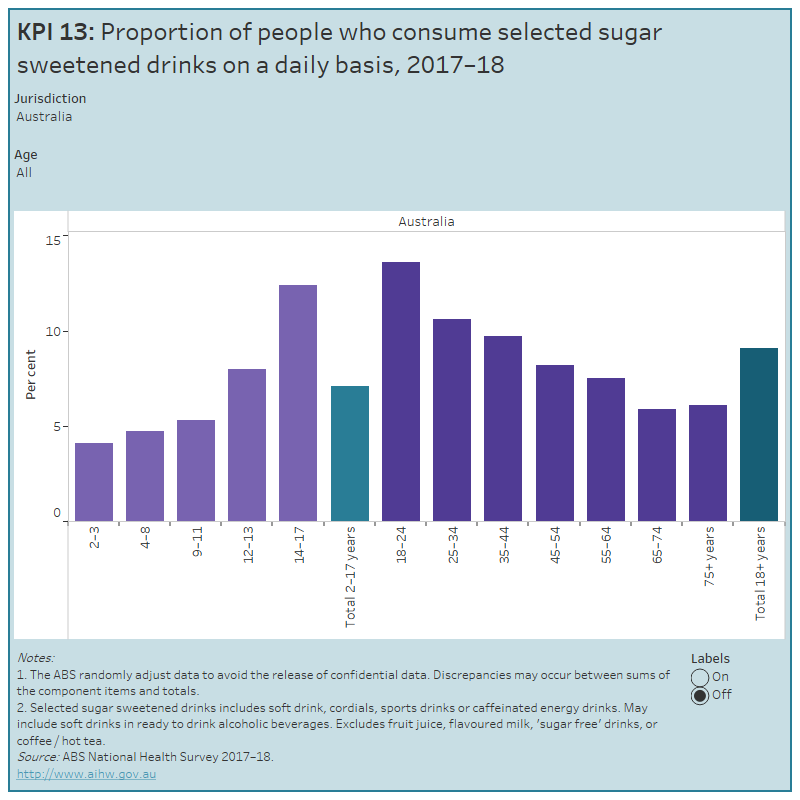
In 2017–18, around 1 in 14 (7.1%) of children aged 2–17 years and around 1 in 11 (9.1%) adults aged 18 years and over consumed selected sugar sweetened drinks on a daily basis. Rates of daily consumption of selected sugar sweetened drinks ranged from 14% for adults aged 18–24 to 5.9% for adults aged 65–74 (ABS 2018).
Explore the data using the interactive below:
KPI 13: Proportion of people who consume selected sugar sweetened drinks on a daily basis, 2017–18
This figure shows the proportion of people who consume selected sugar sweetened drinks on a daily basis. National, state and territory data is presented by age groups for 2017–18. In Australia, around 1 in 11 adults aged 18 years and over consumed selected sugar sweetened drinks on a daily basis.
Data tables available for download.
More information about food and nutrition.
References:
ABS 2018. National Health Survey: first results, 2017–18. ABS cat. No. 4364.0.55.001. Canberra: ABS
COAG (Council of Australian Governments) Health Council 2019. Healthy mouths, healthy lives: Australia’s National Oral Health Plan 2015–2024. Performance monitoring report: baseline report 2017. Victoria: Dental Health Services Victoria.
NHMRC (National Health and Medical Research Council) 2013. Australian Dietary Guidelines. Canberra: National Health and Medical Research Council.
|
Definition |
Proportion of people who regularly consume sugar sweetened beverages and/or confectionary |
|---|---|
|
Desirable rate |
Low |
|
Data sources |
NDTIS(1) |
|
Inclusions |
Survey response |
|
Exclusions |
None |
- Survey questions in NDTIS still under review


