Differential access to hospital procedures
Definition: The number of hospitalisations involving selected procedures per 1,000 population for selected population groups. Data are presented as a number per 1,000 population (age standardised).
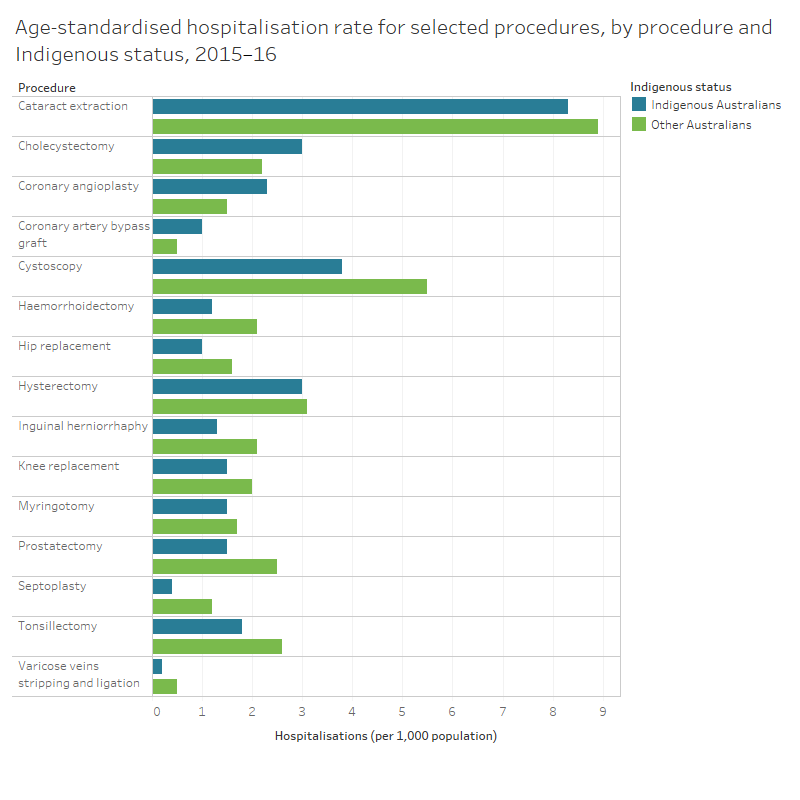
The rates for the selected procedures are presented as an indicator of accessibility. In this case, rates for the selected hospital procedures for Indigenous Australians are compared with Other Australians.
Source: National Hospital Morbidity Database; Table S1.4.35.
- In 2015–16, Indigenous Australians were more likely than Other Australians to undergo a Cholecystectomy, Coronary angioplasty and Coronary artery bypass graft; Other Australians were more likely to undergo all other selected procedures.
- Cytoscopy was the procedure with the largest difference in rates for Indigenous Australians and Other Australians (3.8 and 5.5 separations per 1,000 population, respectively).
- The greatest reduction in differential access for Indigenous Australians since 2009–10 was for Cataract extraction; the difference between Indigenous Australians and Other Australians decreased from 2.5 separations per 1,000 population to 0.6 separations in 2015–16.
- These rates do not take account of differences between Indigenous Australians and Other Australians in the need for procedures, and do not provide information on people who may require a selected procedure but did not have the procedure.
For more information, see Chapter 7.16 'Variation in health care provision'.


