Antenatal care
Antenatal care is a planned visit between a pregnant woman and a midwife or doctor to assess and improve the wellbeing of the mother and baby throughout pregnancy. Antenatal care is associated with positive maternal and child health outcomes – the likelihood of receiving effective health interventions is increased through attending antenatal care. It does not include visits where the sole purpose is to confirm the pregnancy.
Duration of pregnancy at first antenatal visit
The proportion of women receiving antenatal care in the first trimester (before 14 weeks’ gestational age) is the most widely reported indicator of antenatal care. Regular antenatal care in the first trimester is associated with better maternal health in pregnancy, fewer interventions in late pregnancy and positive child health outcomes.
The Australian Pregnancy Care Guidelines (Department of Health and Aged Care 2020) recommend that a woman has her first antenatal visit within the first 10 weeks of pregnancy. In 2021, 60% of women attended antenatal care within the first 10 weeks of pregnancy.
Figure 1 presents data on the duration of pregnancy at the first antenatal care visit of women who gave birth, by selected maternal characteristics, for 2021. Select the trend button to see how data has changed over a 10-year period.
Figure 1: Proportion of women who gave birth, by duration of pregnancy at first antenatal visit and selected topic
Bar chart shows pregnancy duration at first antenatal visit by selected topics and a line graph shows topic trends between 2012 and 2021.
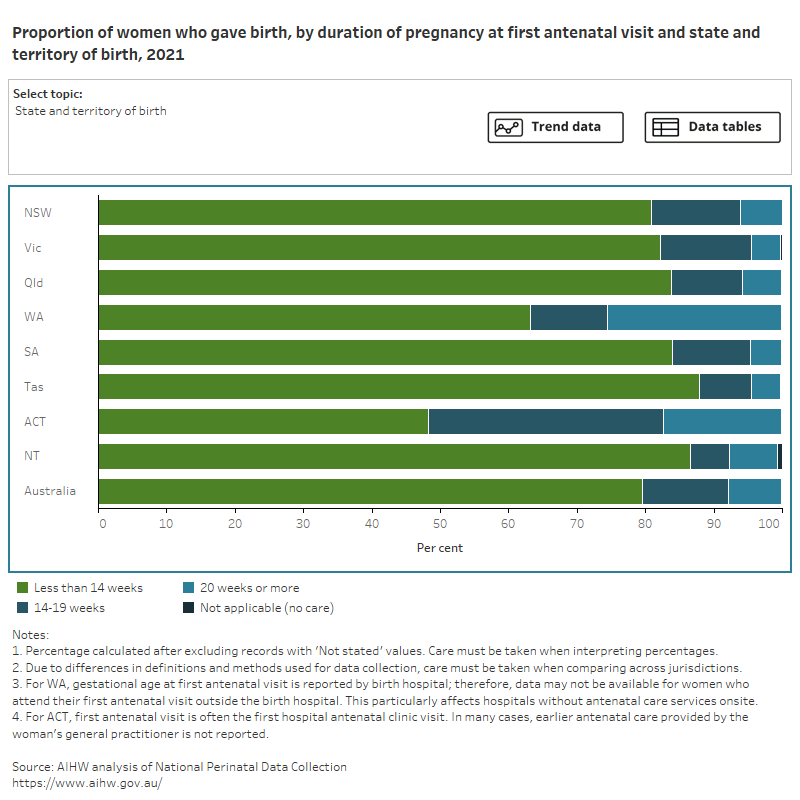
Most women attend antenatal care in the first trimester, nationally (80%) and across all states and territories. Some mothers were less likely to have an antenatal visit in the first trimester, including those who:
- had a parity of 4 or more (66%)
- were aged under 20 (69%)
- smoked during the first 20 weeks of pregnancy (73%) and after 20 weeks (70%)
- lived in Remote (73%) and Very remote areas (68%).
The proportion of mothers attending an antenatal care visit in the first trimester varied across Primary Health Network (PHN) areas and Statistical Area Level 3 (SA3).
Figure 2 presents the number and proportion of women who gave birth who had at least one antenatal visit in the first trimester, by PHN area or SA3, in 2021.
Figure 2: Proportion of women who had at least one antenatal care visit in the first trimester, by selected geography
Map shows proportion of women who had at least one antenatal visit in the first trimester by selected geographies and years.
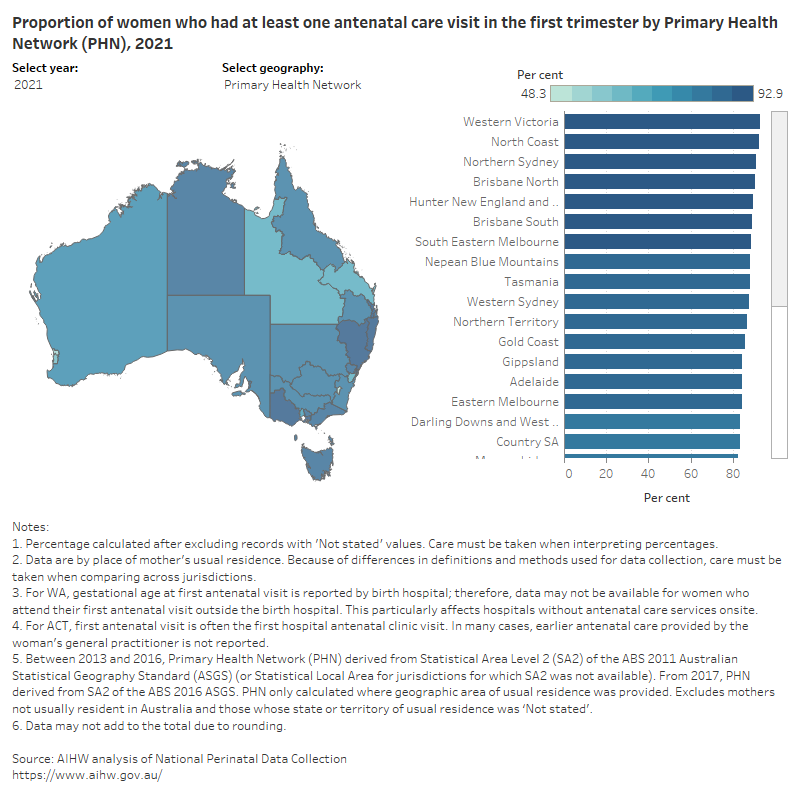
In 2021, the proportion of mothers who attended an antenatal care visit in the first trimester ranged from 48% (in the Australian Capital Territory) to 93% (in Western Victoria) across PHN, and from 32% (in West Pilbara) to 98% (in Barwon – West) across SA3. It is important to note that in the ACT, first antenatal visit is often the first hospital clinic visit and in many cases, earlier antenatal care provided by the woman’s general practitioner is not reported.
For more information on antenatal care in the first trimester by Primary Health Network area or Statistical Area Level 3 see National Perinatal Data Collection annual update data tables 5.1 and 5.7, respectively.
For related information see National Core Maternity Indicator Antenatal care in the first trimester.
For more information on duration of pregnancy at first antenatal visit see National Perinatal Data Collection annual update data table 2.13.
Number of antenatal visits
The Australian Pregnancy Care Guidelines (Department of Health and Aged Care 2020) recommend that first-time mothers with an uncomplicated pregnancy have 10 antenatal care visits during pregnancy (7 visits for subsequent uncomplicated pregnancies). In 2021, 83% of women who have previously given birth attended 7 or more antenatal care visits and 58% of first-time mothers attended 10 or more antenatal care visits.
Figure 3 presents data on the number of antenatal care visits of women who gave birth, by selected maternal characteristics, for 2021. Select the trend button to see how data has changed over a 10-year period.
Figure 3: Proportion of women who gave birth, by number of antenatal visits and selected topic
Bar chart shows number of antenatal visits by selected topics and a line graph shows topic trends between 2012 and 2021.
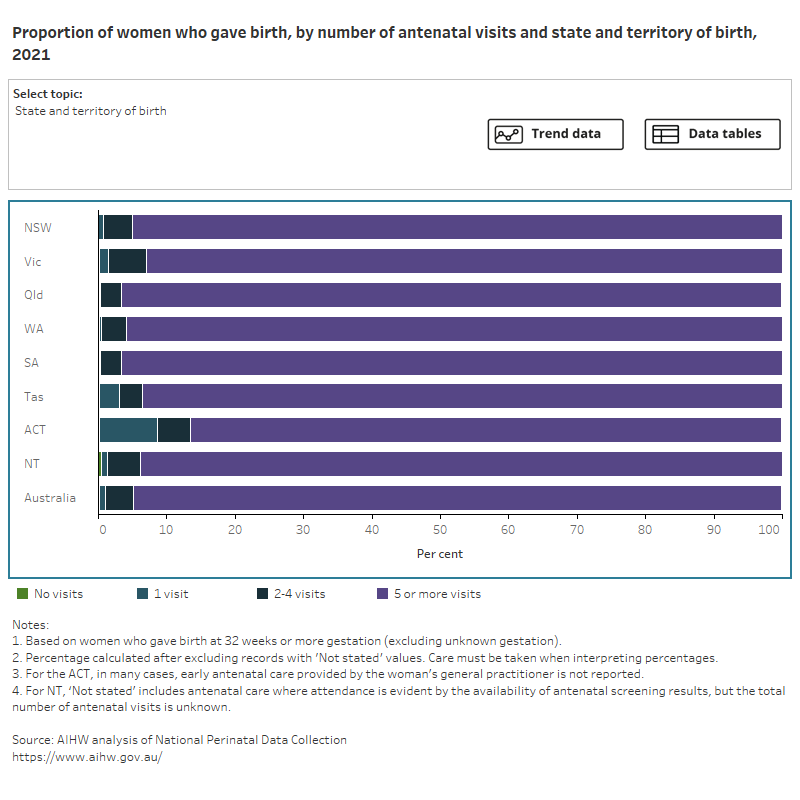
More than 9 in 10 (95%) mothers had at least 5 or more antenatal visits during their pregnancy. This proportion was slightly less among women who smoked in the first 20 weeks of pregnancy (89%) and after 20 weeks (87%), teenage mothers (aged under 20) (90%) and women who lived in Very remote areas (91%) and the most disadvantaged areas (95%).
The proportion of mothers who had 5 or more antenatal visits decreased as the number of previous pregnancies increased (from 96% among first-time mothers to 87% among mothers who had had 4 or more previous pregnancies).
The proportion of mothers attending at least 5 or more antenatal visits varied across Primary Health Network (PHN) areas and Statistical Area Level 3 (SA3).
Figure 4 presents the number and proportion of women who had 5 or more antenatal care visits, by PHN area or SA3, in 2021.
Figure 4: Proportion of women who had 5 or more antenatal care visits, by selected geography
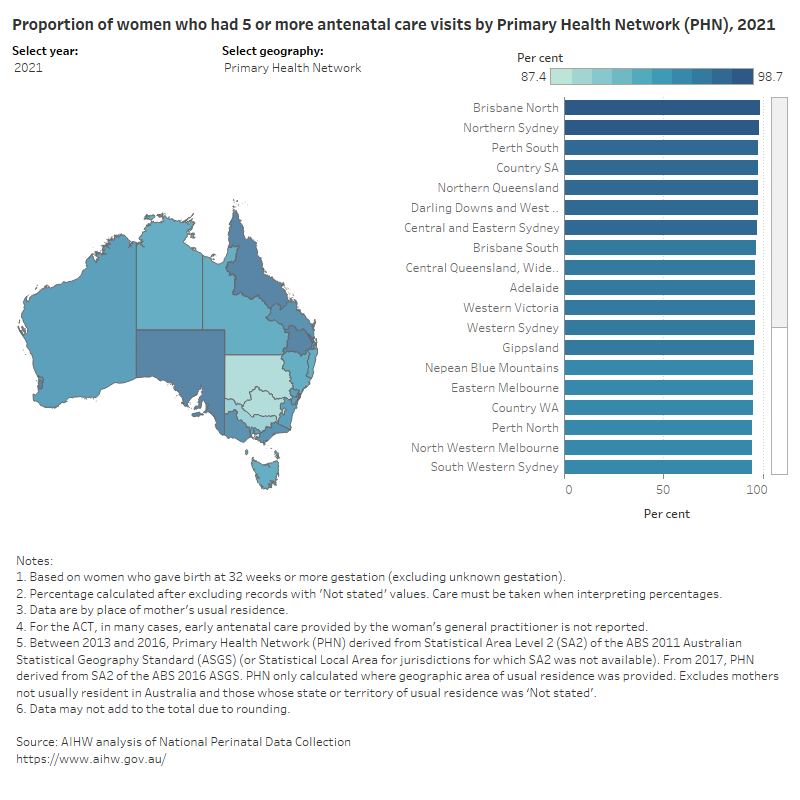
In 2021, a high proportion of mothers attended 5 or more antenatal visits – ranging from 87% (in the Australian Capital Territory) to 99% (in Brisbane North) across PHN, and from 56% (in Frankston) to 99.6% (in Melville) across SA3.
For more information on number of antenatal visits see National Perinatal Data Collection annual update data table 2.12.
For more information on antenatal visits by Primary Health Network area or Statistical Area Level 3 see National Perinatal Data Collection annual update data tables 5.2 and 5.8, respectively.
References
Department of Health and Aged Care (2020) Clinical practice guidelines: pregnancy care, Department of Health and Aged Care, Australian Government, accessed 13 April 2021.


