Gestational age
Gestational age is the duration of pregnancy in completed weeks. The gestational age of a baby has important implications for their health, with poorer outcomes generally reported for those born early. Gestational age is reported in 3 categories:
- pre-term (less than 37 weeks’ gestation)
- term (37 to 41 weeks)
- post-term (42 weeks and over).
The proportion of babies born between 20 and 36 weeks remained steady between 2011 (8.3%) and 2021 (8.2%) with a peak of 8.7% reached most recently in 2018, while the proportion born between 37 and 39 weeks increased (for example, babies born at 38 weeks increased from 19% in 2011 to 23% in 2021) and the proportion born from 40 weeks onwards decreased (for example, babies born at 40 weeks decreased from 25% in 2011 to 20% in 2021).
Figure 1 presents data on the grouped gestational age of pre-term and post-term babies and the individual completed weeks for term babies, for 2011 and 2021.
Figure 1: Proportion of babies, by gestational age grouped by term and completed weeks
Bar chart of proportion of babies by gestational age grouped by term and completed weeks between 2011 and 2021.
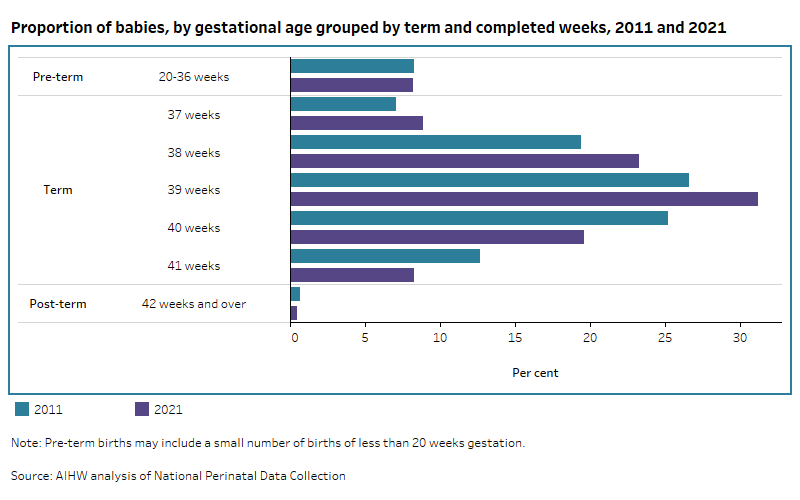
Figure 2 presents data on the gestational age of babies, by selected maternal and baby characteristics, for 2021. Select the trend button to see how data has changed over an 11-year period (where available).
Figure 2: Proportion of babies, by gestational age group and selected topic
Bar chart shows gestational age group by selected topics and a line graph shows topic trends between 2011 and 2021.
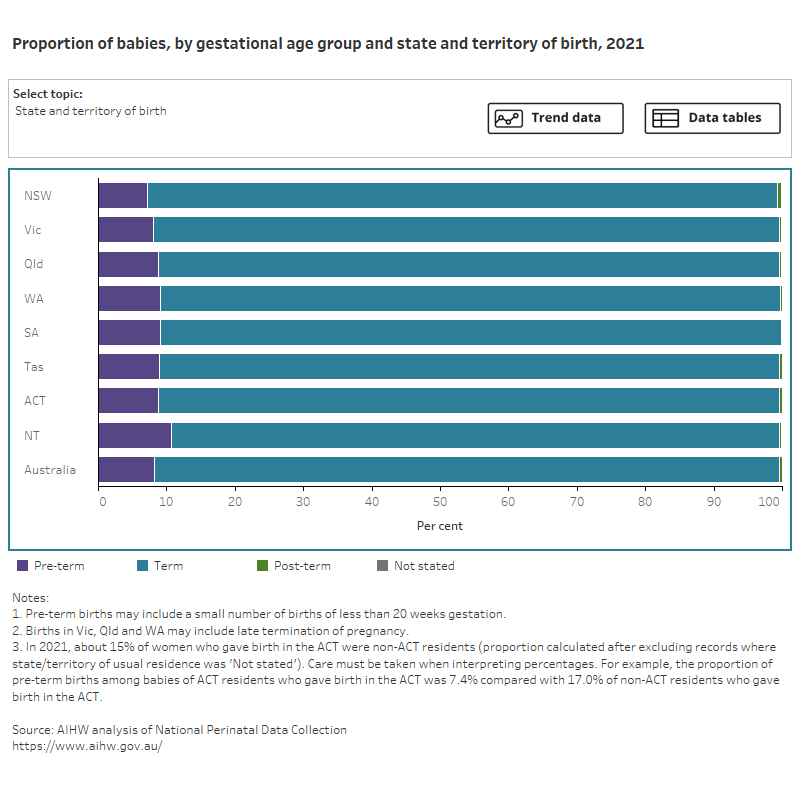
Most babies (92%) in Australia are born at term (37–41 weeks), with 32% at early term (37 or 38 weeks) and 60% at full term (39–41 weeks). This is similar across the states and territories and has been stable over time.
Almost 1 in 10 babies (8.2%) were born pre-term and of these the majority were born between 32 and 36 completed weeks.
Babies born to mothers who smoked at any point during pregnancy were more likely to be born pre-term (13%) than babies born to mothers who had not smoked (7.6%).
Most singleton babies were born at term (93%), while twins and babies of other multiple births were more likely to be born pre-term (57% for twins and 100% for other multiples).
For more information on gestational age see National Perinatal Data Collection annual update data table 3.5.


