Prescription drug dispensing
Data on prescription medicine dispensing in this report are sourced from the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme (PBS). Data from the PBS provide information on the number of prescriptions dispensed and the number of patients supplied at least one script within a given financial year. The PBS database includes information on medicines that may be used for non-medical purposes (including opioids, benzodiazepines and gabapentinoids) and medicines that are used to help people stop their smoking or alcohol consumption (smoking and alcohol cessation medicines). See Box PHARMS 1 for more information on non-medical use of pharmaceuticals and Box PHARMS 2 for information on the PBS.
The following data visualisation contains information on PBS dispensing of selected medicines in Australia from 2012–13 to 2021–22, by drug class and remoteness area or state and territory. Select filters to view the data for opioids, benzodiazepines, gabapentinoids, smoking cessation medicines or alcohol cessation medicines by geographic region or state/territory.
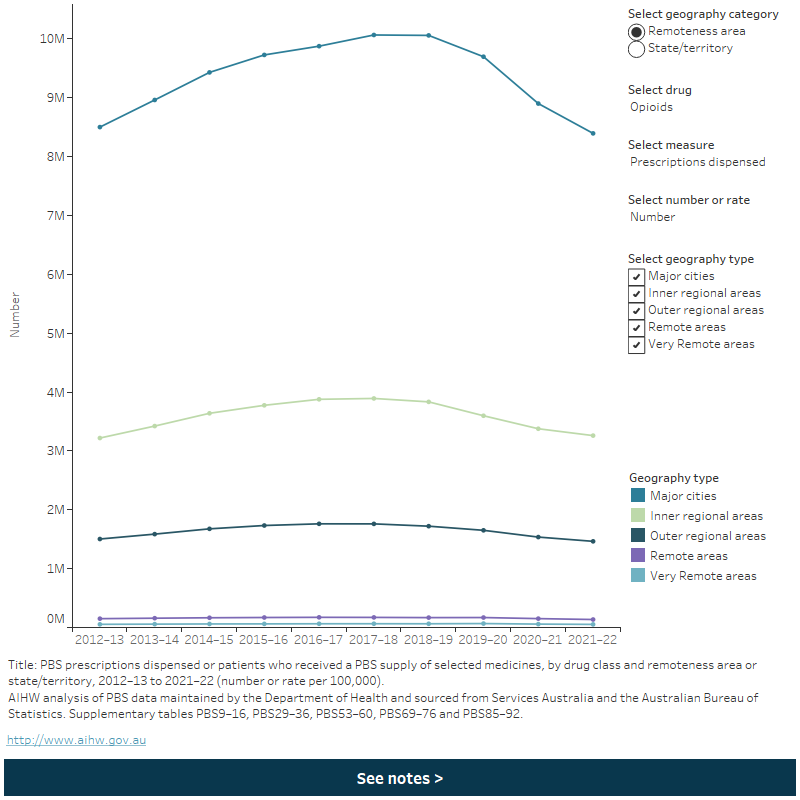
Figure: PBS prescriptions dispensed or patients who were dispensed selected medicines, by drug class and remoteness area or state/territory, 2012–13 to 2021–22 (number or rate per 100,000)
This figure shows PBS prescriptions dispensed or patients who received a PBS supply of selected medicines, by drug class and remoteness area of state/territory, 2012-13 to 2021-22. In 2021-22, 8,392,600 opioid scripts were dispensed in major cities, a decrease from 2020-21 (8,899,215).